2. How does 3D printing work?
To create a 3D printed object, you use an “additive process”. The three-dimensional object is created by laying down successive layers of material until the object is finished.
3. What is 3D printing good for?
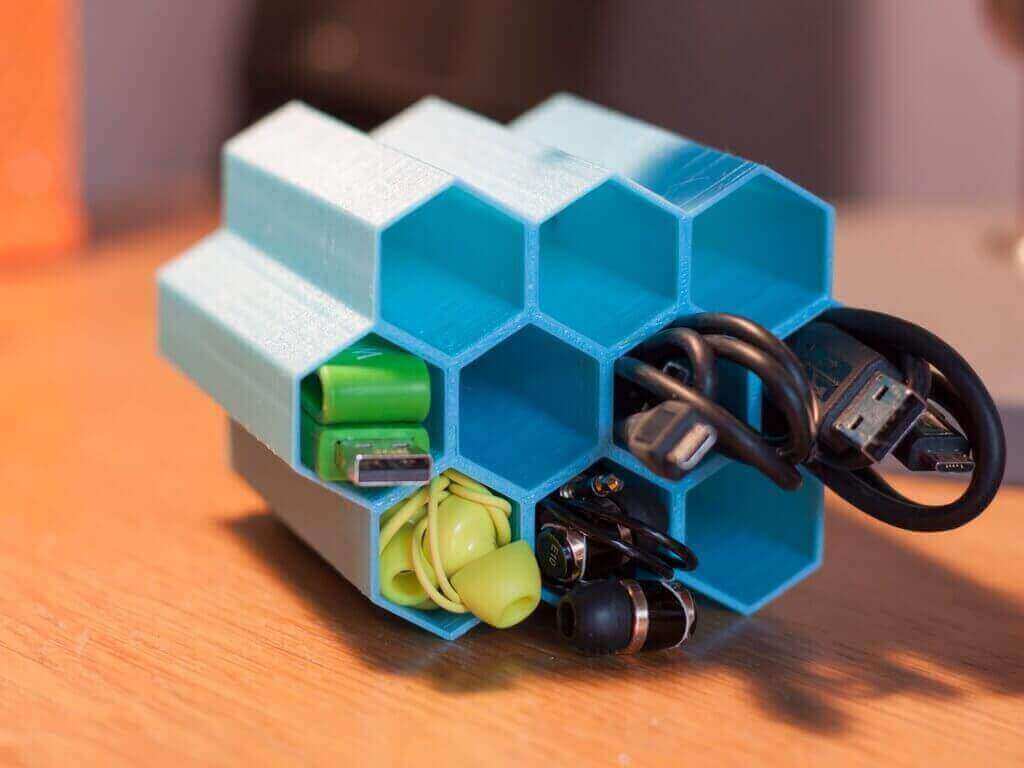

Whether you need a frame for your drone project, simply a door stopper or anything else in between, you can 3D print it. 3D printing is good for making your life easier with simple hacks and ideas. As of November 2016, there are estimated 2 million 3D print files in 3D repositories for you to download.
On the industrial side of things, 3D printing has enabled different industries, from the healthcare to the automotive industry, to do things never before possible and bring products to the market much faster.
One spectacular area where 3D printing excels is in the medical area. Custom-built prostheses, 3D printed tissue are becoming more common in labs.
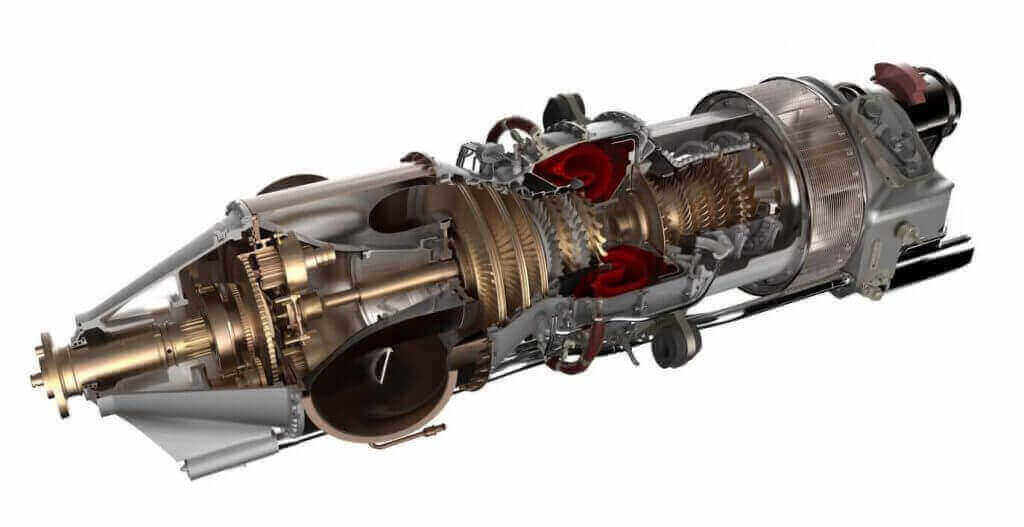
But 3D printing also is strong when it comes to manufacturing small batches of goods. One example: the aerospace industries’ ability to 3D print small jet engine components with complex inner channeling, making the engine more fuel efficient. This would never have been possible with the traditional method of CNC milling.
4. What are the benefits of 3D printing?
Like most emerging technologies, 3D printing offers benefits in a lot of areas. These include improvements in financial, logistical, healthcare, creative and environmental areas.
For one, the technology allows for endless customization with regards to design and material. One notable example of this benefit is in the healthcare sector. Complex prosthetic limbs can be produced precisely to individual needs for a much lower price.
In the area of aerospace, complex parts that take a long time to assemble can now be 3D printed in one go. This speeds up the assembly line and reduces the cost of the finished product. Also, mass production in higher numbers is made possible.
3D printing enables designers to rapid prototype, ultimately saving time in the design process. This allows new or improved products to hit the market much sooner than with conventional means.
3D printers are portable. That allows end products or components to be 3D printed where and when they are needed and thereby lowering or eliminating inventory needs. Satellites, for example, will most likely be 3D printed in space in the future.
Since 3D printing utilizes the concept of adding material rather than subtracting material, the process leaves behind little to no waste. Although materials used in conventional manufacturing methods are recyclable, the process of recycling materials costs money that can be saved with 3D printing.
5. What are the limitations of 3D printing?
Although it is already deeply implemented in the world of prototyping, 3D printing is still some years away from having a breakthrough in the world of manufacturing. This breakthrough would allow 3D printing to spread from just prototyping, with the exception of select components already being manufactured by 3D printers, to being widely implemented in everyday manufacturing processes all over the world.
The main aspect keeping this from happening sooner is the relatively long time it takes to 3D print something that can just as well be manufactured using traditional methods (and we all know that time means money).
3D printing is also limited by the size of the 3D printer. Although there are some pretty big units 3D printing with cement, for example, high-quality and precision parts are limited to smaller machines which can also be very expensive depending on what they are designed to be capable of.
Another limitation is the fact that most 3D printers can only print in one material at a time. Multi-material 3D printers do exist, though, but are not very common yet.
6. Which types of 3D printing technologies are there?
3D printers use one of the following methods to build an object layer by layer:
3D Printing Technology #1: Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
This is the most common technology used in desktop 3D printers. Thermoplastic material is heated and extruded through a nozzle. The nozzle deposits the molten material layer by layer onto a build platform. Each layer sticks to the one beneath it.
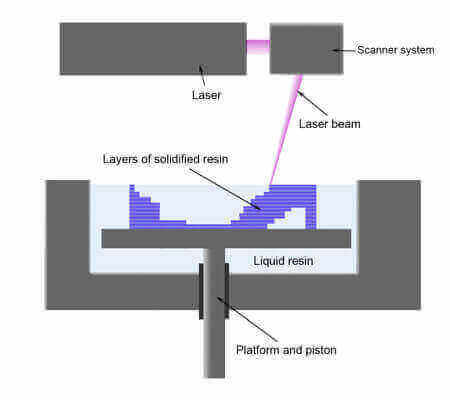
3D Printing Technology #2: Stereolithography (SLA)
The build platform is lowered into a bath filled with a special liquid photopolymer resin. The resin is light-sensitive and becomes solid when exposed to a laser beam. Each cross section of the 3D model is traced onto the layer of cured resin that came before it. This is repeated layer by layer until the 3D object is completed.
In FDM the object is built from the bottom up, in SLA it’s the other way round.
3D Printing Technology #3: Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
This process involves a laser beam fusing powdered material together. The first layer of powdered material is evenly rolled onto the build platform after which the layer of the 3D model is fused together by a laser. Next, the build platform is lowered by the width of one layer, and the next layer of powder is rolled into position. This process is repeated until the 3D object is finished. Since the object is surrounded by (unused) material throughout the duration of the build, support structures are not necessary like they sometimes are with the FDM process.
Many different materials can be used with this technology from plastics to metals.
3D Printing Technology #4: Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
SLS works on the same principal as the SLS process but uses a higher intensity laser and only metal powder. In this process, the tiny metal particles are actually melted together to form a solid piece of metal as if machined from one solid block.
3D Printing Technology #5: Binder Jetting
Binder Jetting also uses a powder bed as its source of material. But instead of a laser, the powder, e.g. metal, is first “glued” together using an adhesive binder after which the object is heat-treated in a kiln to set or fuse the material.
To get colored prints, you can add pigments to the binding materials.
7. Is there a difference between 3D printing and additive manufacturing?
The short answer is no. The term “3D printing” comes from the use of inkjet printer heads (in the first 3D printers) to deposit, either layers of UV-curable photopolymer resin or a binding material onto a layer of powder in a powder bed process. However, the term now universally encompasses all additive manufacturing technologies.
The more technical, or correct, way of referring to the automated process of building a 3D object from scratch using a digital file is “additive manufacturing”.
8. What is the difference between 3D printing and 4D printing?
4D printing is a subset of 3D printing. In “normal” 3D printing, the end product is static, unless some flexible material is used, and it is meant to stay in that form. 4D printing is a way of “programming” the material/object to change form or functionality when given the correct impulse.
For example, running shoes could be designed to change the way they feel or fit depending on the activity of the wearer. Also, clothing could change its functionality depending on the weather. Although these products and solutions are not yet on the market, various research institutions like the MIT Self-Assembly lab are working on improving such technologies.
9. Is 3D printing only good for plastic?
No. 3D printing can be done using with a very wide variety of materials. Literally, just about any material can be 3D printed as long as it has a practical solid state. For example, a gaseous material like oxygen has a solid state, but only at a very low temperature which makes it impractical and pointless to 3D print with.
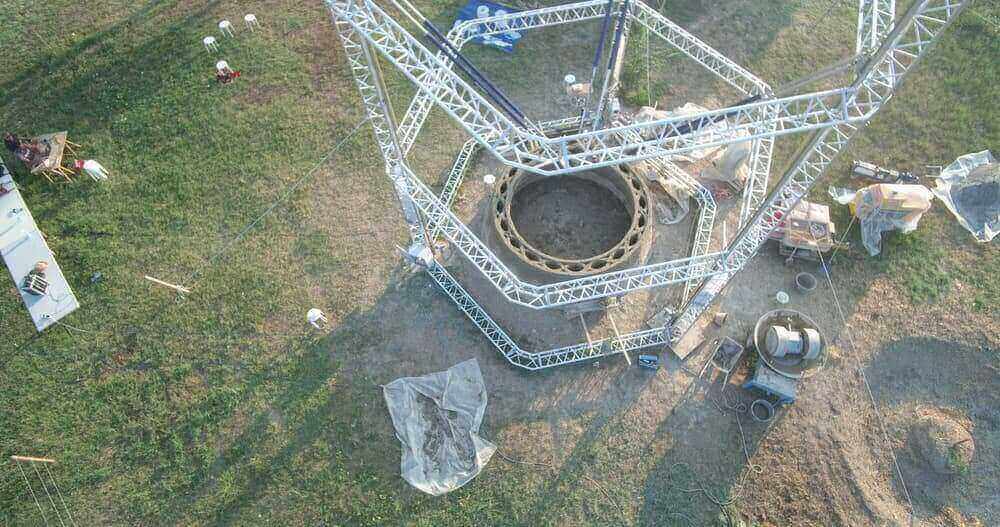
Most desktop 3D printers can only print thermoplastics. But some of these 3D printing filaments can be enriched by adding e.g. wood, metal or other materials. 3D Printing machines as used in 3D printing services can also print ceramics or precious metals. And there are 3D printers used in the building industry that can even handle concrete or clay-straw mixtures. Below you can see a huge WASP 3D printer build a shelter structure in Italy.

10. Are 3D printed goods as good as those manufactured “traditionally”?
This depends on the product in question. Arguably, a 3D printed Japanese kitchen knife will not be as sharp as, or retain its edge as good as an authentic, carefully forged steel blade.
On the other hand, 3D printing has enabled certain products to be improved beyond the capabilities of traditional manufacturing processes like jet engine components.
But on a general level, it would be a subjective statement to suggest that a certain 3D printed product is better or worse than its traditional counterpart. Seen on an economic level, 3D printing is on its way to becoming a very efficient, resourceful, and cost effective means of production and will probably surpass conventional manufacturing processes in those aspects in the future.
11. Are there myths about 3D printing which aren’t true?
Yes, there are a few common myths about 3D printing. Hopefully, this will clear them up.
3D Printing Myth #1: 3D printers cost too much
From the time when 3D printing was invented until the 2000s, it is true that 3D printers could only really be purchased for industrial purposes. But nowadays, high quality, consumer-grade machines are available to anyone at prices under $500 (more information here). There is, for example, a huge selection of DIY 3D printers based on the renowned Prusa i3 printer (pictured below).

3D Printing Myth #2: 3D printers can produce guns
Yes, it is possible to 3D print a gun. But it is a difficult task, and also a dangerous one. A 3D printed plastic gun will only last for a few shot before breaking apart, which can be potentially dangerous to the shooter.
If you are concerned that 3D printed guns are a security issue, know that the cost of making one includes: the purchase of a 3D printer and the materials, the time to 3D print and assemble the parts, and still the bullets. At this point, someone might as well purchase a real gun.
Also, 3D printed guns are banned in several countries, in some you can even go to jail by downloading the blueprints.
3D Printing Myth #3: 3D printing market is still not stable enough
By definition, a stable market is “A market with low trading volume that can nevertheless absorb a large sale without a major change in price. In most low volume markets, a single large sale causes a big jump or drop in price because there are relatively few other sales against which to compare the large sale. The term is most common in foreign exchange.”
Market analysts say that the 3D printing market has already stabilized and will see more stable growth in the coming years than in the past years.
(Sources: Investing News Network, Financial Dictionary)
3D Printing Myth #4: 3D printers can print human organs
Not yet. But researchers are tirelessly working towards that goal. The main problem is that human organs are not only very complex, but also interdependent.
Right now the focus is on being able to print simple tissue for simple organisms. You can find more on the topic here.
3D Printing Myth #5: 3D printing is for large-scale manufacturing
At the moment it wouldn’t make sense to start manufacturing everything using 3D printing technologies. 3D printing simply isn’t fast enough to be profitable on a large scale. The exception is made when custom products come into question. Hearing aids, for example, are highly customized products with special geometric forms. In this case, it is already cheaper to manufacture hearing aids with 3D printing rather than with traditional manufacturing processes.
3D Printing Myth #6: Soon every home will have a 3D printer
Although tempting to believe, 3D printing services are becoming very affordable. This means that for most people, it wouldn’t pay off to purchase a 3D printer for the limited amount of items they might want to print every year.
However, it is too early to tell. Just look at how everybody carries a personal computer around in their pocket.
3D Printing Myth #7: Things are quicker to make on a 3D printer
Although it has become faster, 3D printing still takes longer than most traditional manufacturing processes. Also, reliability is an issue. If the 3D printer screws up, you’ll have to start all over again.
In certain cases, of course, 3D printing would be faster, if the object to be manufactured has a very complex shape and doesn’t need to be mass produced.
3D Printing Myth #8: Some things are cheaper to make on a 3D printer
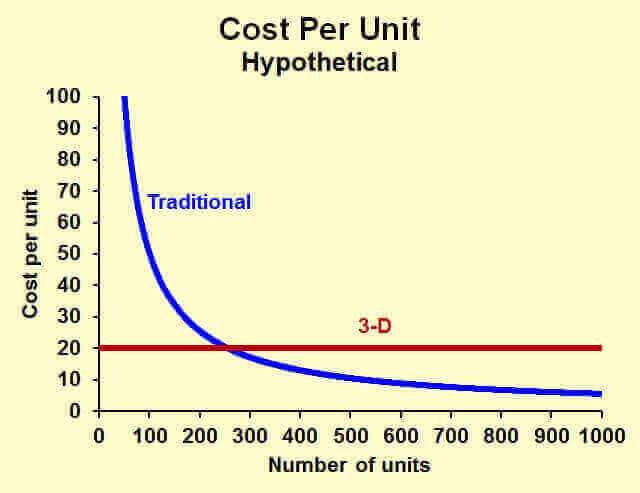
This depends on the number of items you want to produce and the complexity of the product. The cost per item stays the same for whatever amount of items you wish to 3D print. Using traditional means, however, the price of production decreases as the number of items increases. Where the two graphs cross is where the 3D printing and traditional means cost the same.
So: Yes, some things are cheaper to make on a 3D printer.
3D Printing Myth #9: 3D printers will save humanity
No doubt: 3D printing has huge potential for making this world a better place. Some would argue that 3D printing will enable people to cheaply produce high-quality goods and necessities by themselves. However, this will only be the case if the 3D printing industry becomes fully open source. Open source technology does wonders in terms of user accessibility and not having to put up with proprietary products and user licenses.
12. How many 3D printers are there worldwide?
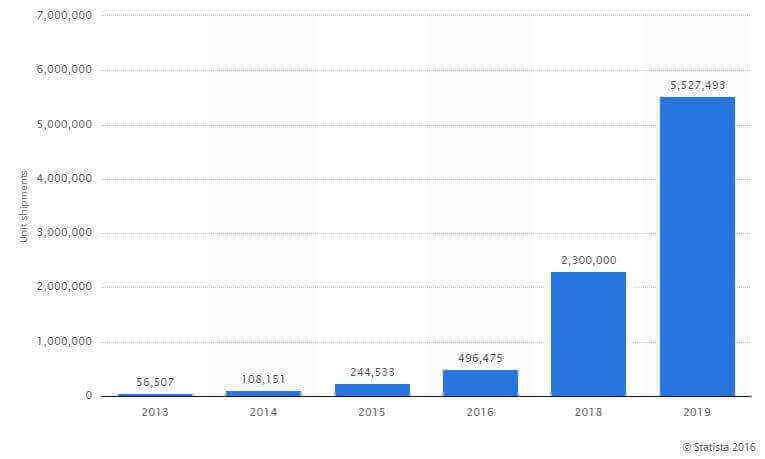
Statistics found on Statista.com suggest that in 2016, there are close to 500,000 3D printers in the world. By 2019, the number is estimated to grow to 5.5 million units worldwide.
13. Who invented 3D printing?
Charles (Chuck) Hull, co-founder of 3D Systems, invented the solid imaging process known today as stereolithography (SLA). This was the first commercial 3D printing method. He first thought of the idea in 1983 while using UV light to harden tabletop coatings. In 1986 he received the patent for the process.
By the way, Charles Hull is also the person who invented the .STL file format, which is the most common 3D printing file format.
14. Can I use 3D printing in education?
Yes, 3D printing is already being introduced to students at an early age.
3D printing enables the physical manifestation of someone’s thoughts and ideas. The hands-on experience makes a technical subject fun and attractive, even for people who aren’t especially interested (yet) in design, architecture, computer science or engineering and many other fields of study. For some, what used to be a dry and theoretical and (as a result of that) boring class, can now become an engaging and hands-on experience.
China, for example, has plans to have every one of its elementary schools equipped with 3D printers by 2017. The early immersion of students to the new technology will make them fit for the future, when 3D printing will become more and more important for the workplace and everyday life.
Also, in Japan, Kabaku and Microsoft have developed a 3D printing and programming learning tool. Based on the popular video game Minecraft, students can design structures in the game and have their creations output on a 3D printer. This helps the students realize the potential impact that their imagination and ideas can have. And makes them realize that designing is a process of trial and error, often involving several iterations before getting it right.
There is no debating whether or not 3D printing can be used in the classroom. It’s more a question of when. For further reading, check out this article on how 3D printing improves education. Also, there is an interesting Teacher‘s Guide to 3D Printing here.
15. Are 3D printing projects on Kickstarter trustworthy?
Most of them are. But unfortunately, there are some black sheep in the Kickstarter community. There has been at least one major criminal case, where Kickstarter funds were misused by one of the project leaders.
Peachy Printer Inc. raised $651,091 dollars in 30 days. However, only $200,000 of that sum ever made it into the company bank account. Confessions made by the company’s co-owner and financial manager revealed that he stole a total of at least $324,716 of the money raised on Kickstarter to build a house for himself. But that might not be the whole story. More money was raised on other crowdfunding platforms to the tune of about $500,000 which the management of the company says was poured into research and development. However, not much of that R&D has been shown off by the company. It remains to be revealed, if that money was also mismanaged or not. Here is more on this: Peachy Printer Funds Stolen to Build a House.
Sure, this is an extreme. More often you will encounter delays in delivery of your Kickstarter or Indiegogo 3D printer.
On the other hand, there have been many successful 3D printing products that started out on Kickstarter including the original Formlabs Form One SLA printer, Zortrax M200, the M3D Micro (image), Printrbot and the 3Doodler printing pen.

Every time you invest money in something, there is a certain risk that something will go wrong. It comes down to how much you trust the authenticity of the project. In this article, we compiled a few clues you should consider before backing a crowdfunding project.
16. Will 3D printing be bigger than the internet?
As 3D printing has only begun to see global acceptance and implementation in recent years, it is too soon to know for certain whether 3D printing will be a life-changer comparable to the internet. After all, when computers were first invented, no one knew the tremendous impact they would have. The same goes for the internet. Growing numbers in the 3D printing industry suggest that the technology is going to be huge, but only time will tell- if the impact going to be “internet-size”.
17. How can I connect with other people doing 3D printing?
If you are looking to meet up with other people doing 3D printing, there are a few different routes you can take. A great place to find people who are interested in the same things as you is www.meetup.com, a social platform designed especially for that purpose.
Another great place is your local Fab Lab. There, you are bound to meet other makers.
18. Are there 3D printing events, trade shows or meetups?
Check out ALL3DP’s 3D printing conference calendar.
3D Printing Guide: 3D Printer Buyers
Interested in getting your own 3D printer? Read on to find out what you should consider before making a buying decision.
19. Can I try 3D printing before buying a 3D printer?
Yes. A FabLab is a great place to try out and use 3D printers without having to buy one. Just look up the nearest FabLabs location near you and buy a membership. A membership for 3D printing costs around €10 per month which is a lot cheaper than buying a 3D printer yourself.
Alternatively, there are a lot of maker spaces, typically in bigger cities. There, you will find at least one 3D printer – and usually some friendly makers who can help you.
20. What should I know before buying a 3D printer?
Check out All3DP’s article of how to buy a 3d printer.
21. Which 3D printer is the best one?
The answer to this question would be very subjective. Basically, different 3D printers are capable of different things. Some are better than others. We have put together buying guides for certain types of 3D printers.
- 20 Best 3D Printers in Fall 2016
- 22 Best Cheap DIY 3D Printer Kits in 2016
- 20 Best Cheap 3D Printers Under $500 / $1000
- 12 Best Resin (DLP/SLA) 3D Printers in 2016
- 25 Best RepRap Prusa i3 Kits in 2016 (DIY 3D Printer)
- 7 Best All-In-One 3D Printers in 2016 (3D Printer, Laser, CNC)
- 8 Cheap DIY SLA Printers (DLP/Resin) from $20
22. Can I build my own 3D printer?
Yes, you can either buy a 3D printer kit or design and build one entirely from scratch. Typically, kit 3D printers are cheaper because the manufacturer saves assembly costs. Below, you see a kit of a Printrbot Metal, which can be assembled and calibrated in just a day.
If you’re interested in building your own 3D printer, take a look at our overview of the best cheap DIY printer kits and at our roundup of the best Prusa i3 DIY kits.
(Fun fact: 12-year-old Amogh designed and put together a working 3D printer out of LEGO, K’NEX and a 3D pen. He then uploaded the design and instructions to Instructables for other people to see and replicate.)

23. What 3D printer should I buy?
Check out ALL3DP’s 20 best 3D printers article. You may also be interested in the best cheap, SLA, cheap DIY or all in one 3D printers.
24. Where should I buy my 3D printer?
You can go through the manufacturer directly. Also, Amazon is a great place to browse, compare and buy 3D printers. Every month, All3DP compiles a list of the most interesting 3D printers and 3D printing accessories you can get from Amazon.
25. What does a 3D printer cost?
Prices range from about $200 for a very basic DIY 3D printer to several thousand dollars for more advanced, higher quality units.
Industrial 3D printers can cost up to several hundred thousand to over one million dollars.
26. Is a 3D printing pen a toy or a serious tool?
A 3D pen is both. On the one hand, 3D pens are not capable of producing precision 3D objects like a “normal” 3D printer which is precision-guided to print exactly what you tell it to. Because of this, a 3D pen can’t be regarded as a serious tool when compared to desktop or even industrial 3D printers.
On the other hand, 3D pens are serious tools when it comes to artists and children having fun creating their next masterpieces.
It remains to be seen if the 3D printing pen craze is merely a phase or here to stay.

3D Printing Guide: Filaments
Everything you need to know about the material you feed most desktop 3D printers with to produce their output.
27. What are 3D printing filaments? What do I need them for?
The word “filament” comes from the Latin word for “thread” which is “filum”. It is used to describe anything that is thread-like in structure.
In 3D printing, filament is the name given to the material used by the 3D printer to print. In printers using FDM technology, the material comes in the form of a filament coiled around a small spool. The filament is then fed into the extruder through a guide tube. Usually, thermoplastics for 3D printers using the FDM method come in the shape of filaments.

Some 3D printers, mostly industrial ones, use material pellets instead of filaments. This brings down the cost of 3D printing material significantly. Other 3D printers, the SLA printer types, use liquid resin instead of strands of thermoplastics.
28. What types of 3D printing filaments are there?
There are many different kinds of 3D printing filaments. First of all, they come in two conventional diameters: 1.75mm and 3.00mm.
The most common materials used in FDM 3D printing are PLA and ABS. They are popular for their ease of use (ABS being a little more complicated to 3D print), and their affordability.
But as far as what materials you can print with are concerned, there are almost no limits. It is possible to print in pure metal, food and all sorts of thermoplastics whereby metal and food don’t come in filament form for obvious reasons. But don’t be confused, if you see a spool of filament that says metal on it. In this case, metal dust is mixed with thermoplastic material for use in desktop FDM 3D printers.
Here is a comprehensive article on the many types of 3D printer filament.
29. What is the best 3D printing filament?
This is a tricky question, as there is no “best” filament. It comes down to what your 3D printer can handle and how it handles it. Finding the “best” filament for your 3D printer could require some trial and error. If you have a popular 3D printer, chances are, someone has already found out what works well with your 3D printer and what doesn’t. Online forums are a good place to look.
Another important thing to consider is what type of filament is best suited for the 3D object you plan to print. Should it be magnetic? Should it glow in the dark? Should it be flexible? All these aspects come into play when looking for the ‘best’ filament.

Here is a maker’s guide to different types of 3D printing filament.
Here is some filament buying advice: Filament advice – 5 things to consider before you buy.
30. Where should I buy my 3D printer filament?
Like with the 3D printers, Amazon is a great place to start. There, you can find and compare products. Amazon supplies nearly every kind of 3D printer filament there is. Also, you can – of course – shop from the manufacturer directly.
31. How do I find out what kinds of filament my 3D printer supports?
You have a few options. The obvious ones are to visit the manufacturer’s website or read the 3D printer manual. The supported filament type should be stated clearly.
Another way is to ask Google. You should be able to find all sorts of people writing about their experiences using different filament types with their 3D printer, even types not explicitly listed by the manufacturer that still work. But keep in mind that the warranty won’t be valid any longer if your 3D printer breaks because of a filament the manufacturer does not support.
Also, some manufacturers lock the users into using the manufacturer-made filaments, which usually comes in a proprietary filament cartridge. This way, your choice of (cheap) filaments is limited; on the other hand, you get the best printing results possible (the manufacturers claim).
32. Will unsupported filaments ruin my 3D printer?
You are well-advised to operate your 3D printer within the guidelines given by the manufacturer. Often, the use of the wrong filament can result in damage done to the hot end of your 3D printer. Generally, make sure not to heat the nozzle to temperatures above the given guidelines and only use filaments listed by the manufacturer.
For example, carbon fiber infused filament will erode the nozzle, if the nozzle is not made of material suited for carbon fiber. (But as 3D printers are modular, you can of course replace a worn-out nozzle.)
3D Printing Guide: Software
3D printing involves different types of software. Read on to find out what you definitely need and what’s nice to have.
33. What software do I need for 3D printing?
To prepare an existing 3D model for 3D printing, you will at least need a 3D slicer. Most 3D printers come with their own slicing software. The most popular open source 3D slicer is Cura, the most versatile Simplify3D.
If you are also interested in designing 3D models yourself or in modifying existing models, you will need 3D modeling software.
34. What do I need a slicing software for?
The slicing software prepares the 3D model for your 3D printer. It slices the 3D model into thin horizontal layers that the 3D printer can interpret and print. It also adds support structures that are necessary for printing overhanging structures. You can have the slicing software automatically add supports or place them manually.
The prepared 3D printing file is usually stored as a .gcode file.
The software also allows you to position the model on the print bed and resize it. It also gives you control over the print resolution, infill and printer settings like nozzle temperature and print speed.
Professional slicing software such as Simplify 3D have a preview mode in which you can do a dry run and check how your model will be printed – without having to wait for hours till the print process has finished. This way, you can correct errors before starting the print process.
When all that is done, the 3D slicer will generate a file, thereby turning the STL or OBJ file into G-code which is readable by your 3D printer. Most 3D slicer software is free to use and is perfectly sufficient for desktop 3D printing.
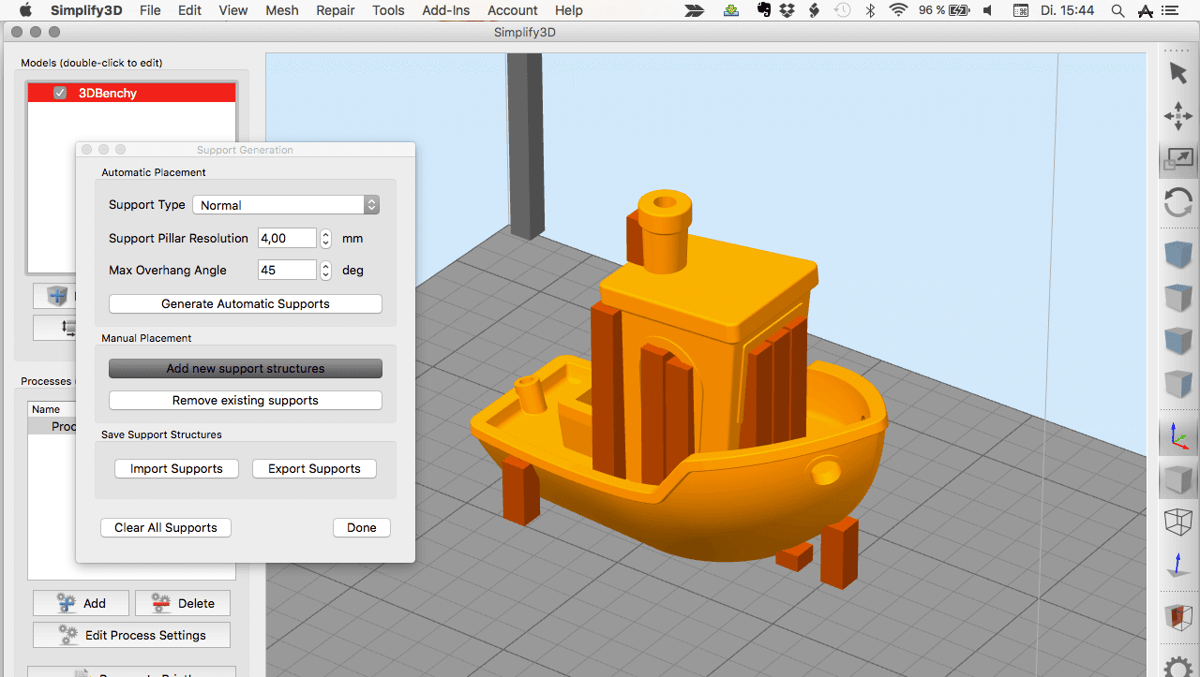
35. What is the best slicing software?
If your printer’s manufacturer did not include a slicing software or if the 3D printing results are not satisfactory, try the free Cura slicing software. Cura was developed by Ultimaker, but it can be used with most desktop 3D printers out there.
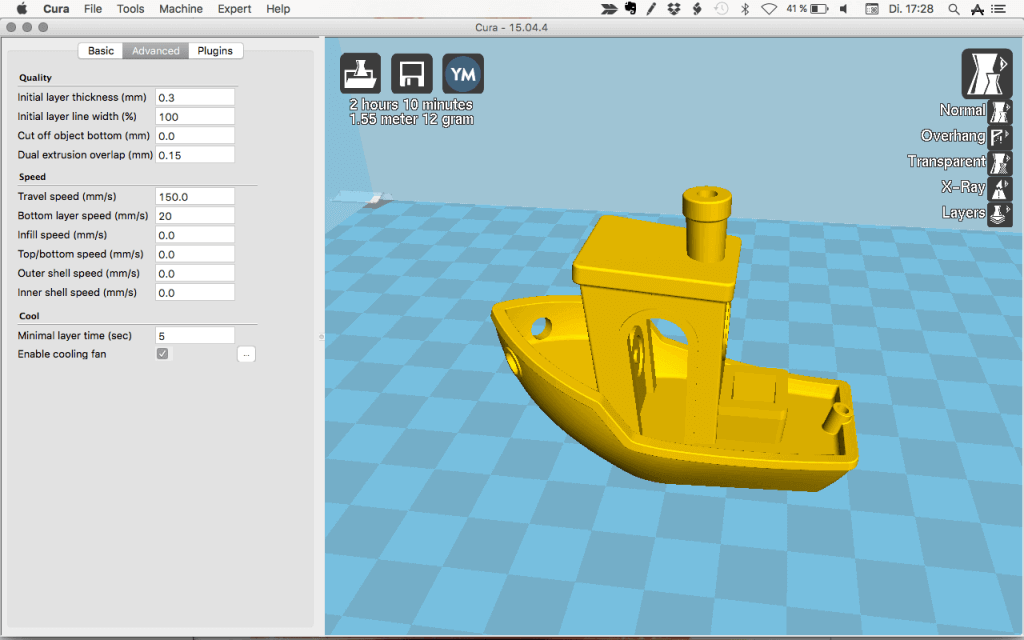
If you’re willing to spend some money, go with Simplify 3D, the best 3D slicing software on the market.
Here is an overview of the most popular 3D slicing programs out there: Best 3D Slicer Software Tools for 3D Printing.
36. How do I create 3D printable models?
First, 3D models can be made using 3D modeling software or real life objects which are then scanned and turned into 3D model files with specialized software often provided by the manufacturer of the scanning device. After that, the 3D models need to be passed through a 3D slicing program to become a 3D printable model.
37. What is the best 3D modeling software for beginners?
For beginners, the software should be intuitive and not have too many pro features. An overload of features will likely confuse and frustrate the beginner. Also, a beginner might not yet know if they want to get into 3D printing for the long haul or not. In this case, we recommend you try a free 3D modeling software.
- 3D Slash is a free and easy-to-use 3D modeling software for Windows and MacOS and for your web browser. In 3D Slash you build your model using a simple building-block concept – like in Minecraft. Here is an in-depth review , and here you’ll find a 3D Slash tutorial taking you from beginner to expert.
- TinkerCAD is a free web-based modeling software. Here, you can build your model from basic shapes and (unlike 3D Slash) by creating geometrical shapes in 2D and turning them into 3D. TinkerCAD is more similar to professional 3D modeling software (compared to 3D Slash) and makes it easier to switch to a more powerful tool later. Here is a short tutorial on how to create a simple name tag.
Other choices for beginners are:
38. Where can I learn how to use a 3D modeling software?
Usually, the developer will provide intro/user tutorials for their software. They will either come in the form of a digital user guide or video tutorials hosted on the company’s website or on YouTube.
Here is a guide pointing you to the best free resources for learning 3D modeling skills.
3D Printing Guide: Models
If you want to 3D print an object, you need a 3D model of that object. Here we’ll explain everything you need to know about 3D printing models.
39. What is a 3D printing model?
A 3D printing model is a file that a 3D printer can read and interpret. It is used to tell the 3D printer where to put the nozzle in order to create the physical object. The model file contains geometrical information that will have to be interpreted by a slicing software that turns the geometrical input into commands the printer can process.
40. What are the most common 3D printing file formats?
There are quite a few 3D printing file formats. Here are the most common ones.
- STL: This is the most popular 3D model format, all slicing tools support it. Here is a more detailed overview of the STL format and how it works.
- OBJ: Also important – and also supported by all major slicing tools – is the OBJ file format. In contrast to STL, OBJ is able to store color and texture profiles; we guess it will become more popular when multicolor printing takes off.
- PLY: PLY, the Polygon file format, was originally used for storing 3D scanned objects.
- 3MF: 3MF is a new file format developed by Microsoft, Autodesk, HP and Shapeways. It is not clear if this will be widely adopted – we’ll have to wait and see.
41. How to start if I want to design a 3D print model?
You are going to want to download and install a 3D modeling software. You don’t have to go and buy the most expensive one on the market. In fact, you don’t need to buy one at all. There are lots of good, free 3D modeling programs out there that are perfect for beginners. Start with simple models, like a cube, then work your way through more complicated objects.
Here are step-by-step tutorials for learning 3D modeling using
42. How can I modify an existing 3D printing model?
You can modify existing 3D models by importing the file into a 3D modeling program. From there you can make all the changes you want. When you are done making changes, remember to save your progress and export the 3D model if you want to.
There are also special tools for editing STL files that are not full-blown CAD programs – and therefore are easier to use.
Here is a detailed guide on how to edit and modify STL files: 5 Free STL Editors + How to Edit STL Files
43. Where do I get free 3D printable models?
Thingiverse is a large and popular 3D file sharing platform. By number of available designs, it is the largest 3D file sharing platform. Anyone can join to upload 3D models and anyone can browse and download files for free.
Here is a list of free 3D model file sharing platforms: The Best Sites for Free STL Files/3D Printer Models
44. Which 3D models cannot be 3D printed?
There are a few conditions a 3D model has to meet to be 3D printable. For example: If the walls of the object are too thin or the geometric nature of the object is physically infeasible, then you are going to have a bad time.
On a more technical note, the 3D model must be “water tight”. This means that there may not be any holes in the mesh of the 3D model. If you have holes (missing information) in the mesh, your 3D printer won’t know what to do, and your 3D print will not finish.
Non-manifold geometry is another design flaw. Non-manifold edges, for example, are edges that share the corner. At this point in the design, the wall thickness is virtually zero.
Here is an article on what could go wrong with your 3D model and how to fix the problems: 12 STL Repair (Off/Online) Software Tools. STL repair tools such as the free MeshFix detect design flaws in 3D models such as holes (see image) or non-manifold elements and correct them:

45. What is the minimal wall thickness of a 3D printing model?
When deciding on the wall thickness of your print, there are a few important things to keep in mind.
First of all, if you have an extremely detailed model of a building, for example, scaling the model down for 3D printing will scale every aspect of the model down including minuscule details and wall thicknesses. There comes a point where the 3D printer is no longer capable of printing such fine details. That can result in super fragile prints and missing details. Therefore, while preparing a file for printing it is important to know which parameters to alter in order to ensure a good result.
The next aspect to consider is the material and technology you are using. Certain materials will remain stable at thinner wall thicknesses than others. User guidelines should be provided by the filament manufacturer.
Using FDM technology, the minimum wall thickness typically lies between 0.05mm and 0.1mm – depending on the resolution your 3D printer supports. However, this doesn’t mean that walls printed at that thickness will be stable at all.
The shape of your 3D model is also a critical aspect. For example, if your 3D model has a part with a lot of overhang, the structures supporting that overhang will need to be thick enough not to warp or break. Also, you need to make sure that supporting walls are strong (thick) enough to hold the weight above it. Generally, 1mm is the lower limit for wall thickness and 2mm is recommended.
46. Why has a 3D printing model to be watertight?
“Water tightness” in a 3D printing model refers to the mesh of the 3D model. The mesh itself must not have any holes. Otherwise, the 3D printer may not be able to print the model. This kind of problem can be fixed using a 3D model repair tool.
More on this topic: 12 STL Repair (Off/Online) Software Tools – Some are Free.
47. Are 3D printing models copyrighted?
Yes, some 3D designs are copyrighted. The UK government has just extended the copyright for industrially manufactured artistic works to the life of the designer plus 70 years (it used to be 25 years before). This prohibits individuals from freely copying a design and 3D printing it with their own tools and resources.
More on the legal status of 3D printed objects: Legal 3D Printing Eagle: Interview with Michael Weinberg.
More on this topic of design stealing: Makers in Uproar over Thingiverse Models on eBay.
48. Can I use a 2D photo to get a 3D printing model?
Yes, but results will vary. Also, it really depends on the scanning method you’re choosing. Many 3D scanning devices use a series of 2D photos to build or create an actual 3D model of the object being scanned.
Also, most of the 3D printed figurines are made from a multitude of 2D photos, which are stitched together.
“Scandy” is an app where the user can take 360° panorama pictures. The pictures can then be 3D printed in color in the form of a sphere. This allows for a more immersive viewing experience of the photo. The app also allows the user to take 3D photos for creating 3D models of people, animals or objects. And if you want to have your model 3D printed, Scandy prints and ships the 3D print to your home.
- Scandy App Turns 3D Photographs into 3D Printables
- 3D Selfies: Enter to the Photo Studios of the 21st Century
49. Who can design a 3D printing model for me?
If you do not know anyone who knows how to handle a 3D modeling software (CAD software), e.g. architects or 3D designers: Look up your local 3D printing service bureau and have them design a specific object for you.
50. How can I protect my 3D printing design from being stolen?
You can place your 3D printing designs under copyright protection law, but that doesn’t keep them from being stolen, once the design makes it online. If your design has been stolen for profit or the copyright is otherwise being infringed, your only course of action are to issue a DMCA takedown notice or to take legal action.
Many startups are working on implementing copyright management into 3D printable object. But there is no gold standard yet.
You can also place your 3D design under a Creative Commons, non-attributable license, which allows other people to copy, redistribute, remix, transform and build upon the design. However, the user must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license and indicate if changes were made. This license does not permit commercial use of the material placed under the license.
More on Creative Commons and 3D printing.
3D Printing Guide: Do It Yourself
51. What should I know before starting 3D printing myself?
Pay close attention to the chemical compounds your 3D printing materials are made of.
- ABS 3D printing material is known to emit toxic fumes (known as VOCs, Volatile Organic Carbon)while printing.
- PLA is considered to be non-toxic while printing.
But as there are many different kinds of 3D printing materials, it is always best to inform yourself about the health hazards of the material you are using even if it is labeled PLA. The reason: There are many different blends of PLA filament which could contain materials that become toxic when heated for printing.
More on 3D printing health concerns: 3D Printing and Toxic Emissions: Everything You Need to Know.
It is likely that your 3D prints won’t always be 100% perfect. Careful calibration of your 3D printer and slicer software setup is essential for successful results. Often, the process of setting everything up properly is a journey of trial and error. Find a good 3D printing online forum where you can ask questions and have them answered by more experienced makers. Also, if you choose a popular 3D printer, there is likely to be a lot more support for that printer, both online and from the manufacturer.
Here are some tips on setting up your slicer program: 3D Slicer Settings for Beginners – 8 Things You Need to Know.
Think about what kind of 3D printer you want. If you’re just getting into 3D printing, we suggest using an FDM (fused deposition modeling) 3D printer. The FDM machines and materials are less expensive than SLA (stereolithography) 3D printers. Those are the two most common options for a consumer looking to get into 3D printing at home.
One major difference within FDM 3D printers is whether or not the printer has a heated print bed. A heated print bed is necessary for printing with ABS filament, whereas a non-heated print bed is sufficient for PLA filament (though a heated bed will improve print quality).
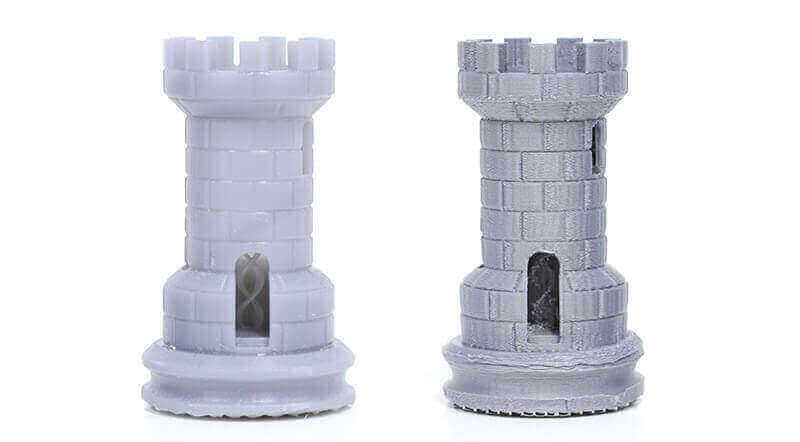
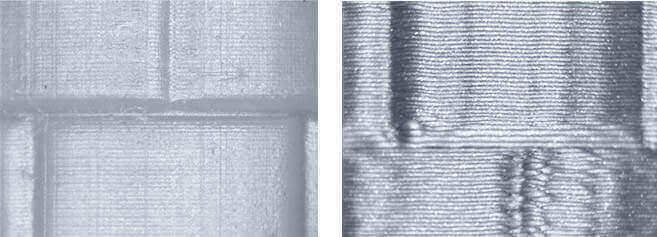
Here is an article explaining the differences between FDM and SLA 3D printers.
These 2 images show that SLA printers are able to produce finer details than FDM printers:

52. What are the most common problems with a 3D printer?
Some of the most common problems in 3D printers are caused by poor setup or lacking quality of the 3D printer. One of the problems is warping, which is caused by rapid cooling of a 3D printed object after or during printing, as thermoplastics like PLA and ABS shrink slightly when they cool down.
Another typical problem is first layer adhesion. Depending on the type of print surface you are using, it could be necessary to add a layer of glue or adhesion spray to the surface in order to increase first layer adhesion (and be careful with hairspray – it’s flammable!). ABS requires a heated print bed for the first layer to adhere to the print surface.
Here is a detailed guide to Common 3D Printing Problems & Troubleshooting.

53. Where can I find a 3D printing tutorial?
Here is a list of the 10 best 3D printing tutorials on the web.
54. How can I reduce my 3D printing costs?
There are several ways to reduce your 3D printing costs. Variables such as material, size, and infill of your print can make a huge difference in price over time, if they are optimized.
What also makes a difference is deciding whether or not you want buy your own 3D printer or use a 3D printing service. For one-time prints it will be cheaper to use a service. But if you want to do a lot of 3D printing, it might pay off soon to buy your own 3D printer and materials.
Here is an article on how to reduce 3D printing costs.
55. Can I do 3D printing with my kids?
Yes, you can do 3D printing with your kids. But never leave them unattended! Hot components like the nozzle and (sometimes) the print bed can seriously burn skin. Moving mechanical components are also dangerous components as they could pinch a child’s finger in no time. But if you take precautionary measures, 3D printing with kids can be a rewarding hobby.
- 3D Printing with Kids: What You Need To Know
- Simple Things to 3D Print with Your Kids
- Funny 3D Printed Bathroom Accessories For Kids
- $25 “3D Printer” Made for Kids
- 3Doodler Start: A Safe 3D Printing Pen for Kids
56. How long does 3D printing take?
That’s totally depending on the quality settings, infill, and size of your 3D print as well as the 3D printing technology used. 3D printing in general takes some time – we’re talking hours, not minutes.
Assuming your using an FDM printer, a 3DBenchy (3D printer test benchmarking model) takes anywhere from one to two and a half hours to complete, which is quite a long time considering the the object is about half the size of a bar of soap.

57. How to 3D print text or nameplates?
This sounds pretty standard but could be quite difficult if you have no experience using 3D modeling software. Many 3D modeling platforms have a function to use text, even in different fonts. It is important to note that with 3D printing, you need a suitable base. This will keep the letters in place and from falling over.
Here are some tutorials covering the basics in different 3D modeling software:
- How to 3D Print Letters or Text using FreeCAD
- How To 3D Print Text Using SketchUp
- Blender Tutorial for 3D Printing: How To 3D Print Text
- 3D Slash Gets Text and Logo Modes
- 3D Printed Business Cards: How to Make Your Own Portrait Card
3D Printing Guide: Technical Questions
So you want to start 3D printing on your own? Here are a few things you may want to consider before firing up your printer.
58. Which materials can be 3D printed?
Printing is possible with a lot of materials. Most commonly known, desktop 3D printers can print with any number of thermoplastic and thermoplastics mixed with other materials like wood fibers, metal powder, glow in the dark compounds and much more. But beyond that, scientists are even experimenting printing with biomaterials in an effort to eventually be capable of 3D printing human organs for transplants.
More on 3D printing materials:
- 28 Great 3D Printer Filament Types (A Guide)
- PLA Filament Guide: 32 Unique Types to 3D Print
- What kind of materials can I use in 3D printing?
59. Which materials can’t be 3D printed?
It’s hard to think of a material that can’t be 3D printed. Theoretically, given the right circumstances, nearly any material can be 3D printed. But practically speaking, liquids for example can’t be 3D printed, unless the room you are 3D printing in is at least below 0°C and you’ve equipped your 3D printer with the necessary modifications to do so. Other materials like naturally gaseous materials also can’t be 3D printed under normal conditions.
60. Is 3D printing in full color possible?
Yes, 3D printing in full color is possible. But the machines are still very expensive. An affordable way to get something 3D printed in full color is to use a 3D printing service. The most common material is binder-jetted gypsum powder, which is then colored in CMYK (like on an inkjet printer).
The most common material is binder-jetted gypsum powder, which is then colored in CMYK (like on an inkjet printer). One of the trends is it to mix 3D printing materials in one printhead, so you get gradients from two or more filaments.
More on full-color 3D printing:
- Hydrographic Printing: Affordable Full-Color Prints for Everyone
- RoVa4D Full Colour Blender 3D Printer on Kickstarter
- Color 3D Printing: Autodesk and Samsung Enter the Arena

61. What resolution can a 3D printer print?
The Resolution of a 3D printer is divided into two parts. First, there is the XY resolution which is the smallest movement the nozzle can make on the X and Y axes. Secondly, there is the vertical resolution which is the minimum layer thickness the 3D printer can be set to. That is the case for FDM 3D printers.
Maximum resolution (quality) varies deeply depending on the 3D printing method being used.
Click here for a detailed breakdown of this topic.
62. What is the best way to 3D print fully functional parts?
The best way to have fully functional parts printed in good quality is to use a professional 3D printing service. To ensure the service can actually produce your design, it would be a good idea to contact the company’s customer support.
Here is a list of professional and community-based 3D printing services.
63. What are the benefits of 3D printing compared to injection molding?
One major benefit of 3D printing compared to injection molding is the cost advantage. Injection molding requires a mold to be manufactured or formed first, which is a costly and delicate process. However, since injection molding costs decrease with increasing production volumes, there usually comes a point where injection molding makes more sense.
Also, some geometric shapes that are 3D printable simply can’t be manufactured using injection molding.
64. What are the differences between 3D printing and CNC milling?
The major difference between 3D printing and CNC milling is the starting point: With 3D printing, the manufacturing process starts from nothing, objects are built by adding material layer by layer. In CNC milling, the process starts with a block of material and is finished by removing material until the desired shape has been formed.
Here is an article explaining the differences between 3D printing and CNC milling.
65. Is 3D printed gold as valuable as “normal” gold?
First of all, gold is not a 3D printable material. Still, 3D printing is used more and more to make gold objects by 3D printing a wax model, which is then cast in solid gold. In other words, your gold, 3D printed or not, will be as valuable as the current market price for gold. In some cases, handmade jewelry by certain famous jewelers will sell for much more than their weight in gold.
3D Printing Guide: Applications
Given the right 3D printer for the job, you can have virtually anything 3D printed: from plastic toys to houses or spacecraft engines.
66. What can 3D printing be used for?
When 3D printing was first invented, it’s only purpose was to create prototypes, hence the technical name “rapid prototyping”. 3D printing offered a quick and cost effective solution to produce multiple iterations of a design prototype, ensuring satisfaction before the product has even been conventionally manufactured even once.
Even though a very large portion of all 3D printing is still focused on rapid prototyping, the technology is now being used in many different areas and even to manufacture end products and components.
So, what can 3D printing be used for today and in the future? Some of the applications are:
- Printing accessories such as smartphone cases and stands, cable holders, boxes, etc.
- Printing replacement parts for household devices, electrical devices, computers, cameras, even bikes and more.
- And even printing parts of a 3D printer.
- Printing toys and tools of all sorts.
- Printing art and jewelry.
- Printing fabrics for creating clothes or even shoes.
- Printing 3D selfies.
- Producing equipment in space.
- Bioprinting (e.g. prosthetics and even artificial organs).
- Printing food.
- Printing houses or house parts.
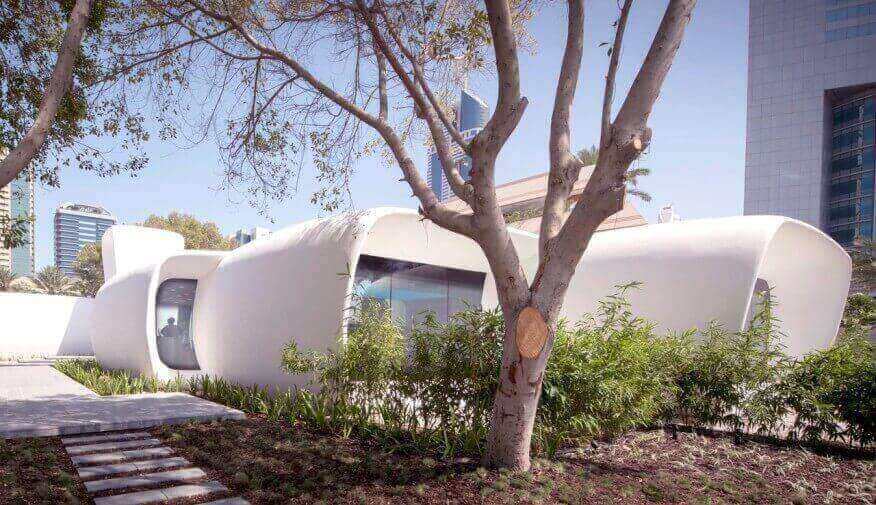

67. What is not suitable for 3D printing?
When it comes to 3D printing, a lot is possible – but even more still isn’t possible. Using an FDM 3D printer, you can not achieve an industrial-grade polished surface. This has to be post-processed.
- Using an FDM 3D printer, you can not achieve an industrial-grade polished surface. This has to be post-processed.
- Now on a hypothetical level, it is not yet possible to 3D print a functional, complex electro-mechanical machine or product (like a car) in one go, even though individual parts can be 3D printed no problem. But researchers are already working on “production 3D printers“.
- Also, bioprinting is not advanced enough yet to 3D print fully functional customized human organs on more than an experimental basis. That technology may still be some years off.
68. How will 3D printing affect the medicinal sector?
3D printing is being used in just about every area of the medical world.
At the moment, it is not yet possible to 3D print fully functional organs for humans but the research is being done. A heart valve that was printed at Cornell university will soon be tested in sheep but that is just one component of the heart, not the whole thing.
Bioprinting isn’t the only medical application for 3D printing. Knee and hip implants or any kind of customized implant that isn’t a complex organ or tissue, can be and is already being 3D printed. Another example is the creation of skull implants for damaged or crushed skulls.
3D printing has significantly lowered the cost of prosthetic limbs. What used to be a complex process of molding and forming can now be replaced by scanning and printing. This process has been made so cheap and efficient that people left crippled by war can now afford to have prosthetic limbs 3D printed. This was made possible in part to research done at the University of Toronto together with Autodesk Research and CBM Canada – and several other people.
Other areas of application include 3D printed hearing aids, shoe insoles, dental implants, special medical instruments and tools and customized case specific solutions.
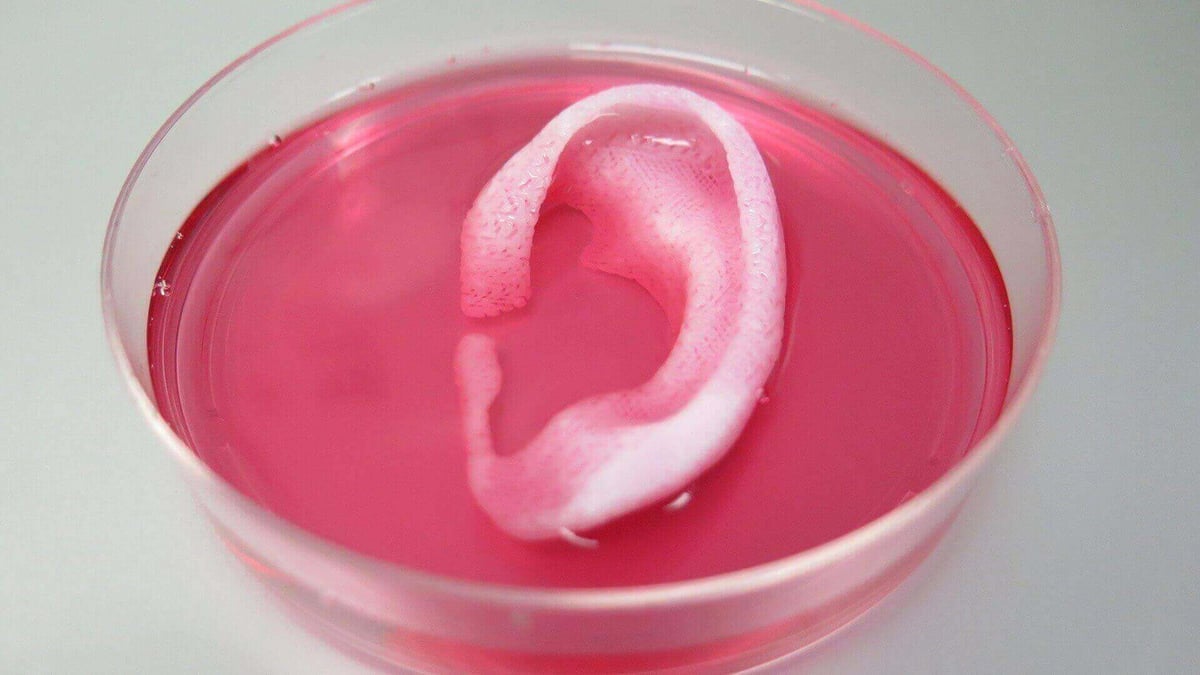
69. What is 3D bioprinting?
3D bioprinting refers to the science of 3D printing living, functional tissues, bones and organs for medical purposes. This field of research, however, is only in its pioneering stages. But experts expect it to be big in the not so far future.
70. How can 3D printing be used in space?
If 3D printing is having such a profound effect here on earth, then it must also have an effect in space travel as well?
Well, it does. In a series of tests, NASA has 3D printed a total of 13 different designs and 20 objects on the ISS. The 3D printed objects include, among others, a wrench and a ratchet. One design file was even sent from Earth to the ISS proving that 3D printing leaves room to improvise. That means, the astronaut’s resources are not strictly limited to what is launched into orbit (except for the filament). NASA has stated that the ability to 3D print on-demand parts and tools is critical for longer missions to Mars.
The Russian Space Agency has announced their solid plan to 3D print a permanent lunar base on the moon in collaboration with ESA, the European Space Agency. The goal of the project is to provide shelter for astronauts, while they look for water on the dark side of the moon. An unmanned mission named “Luna 25”, which is scheduled for launch in 2021, is supposed to scout out the moon for a suitable location and oxygen generating materials. The manned mission is scheduled for 2029.
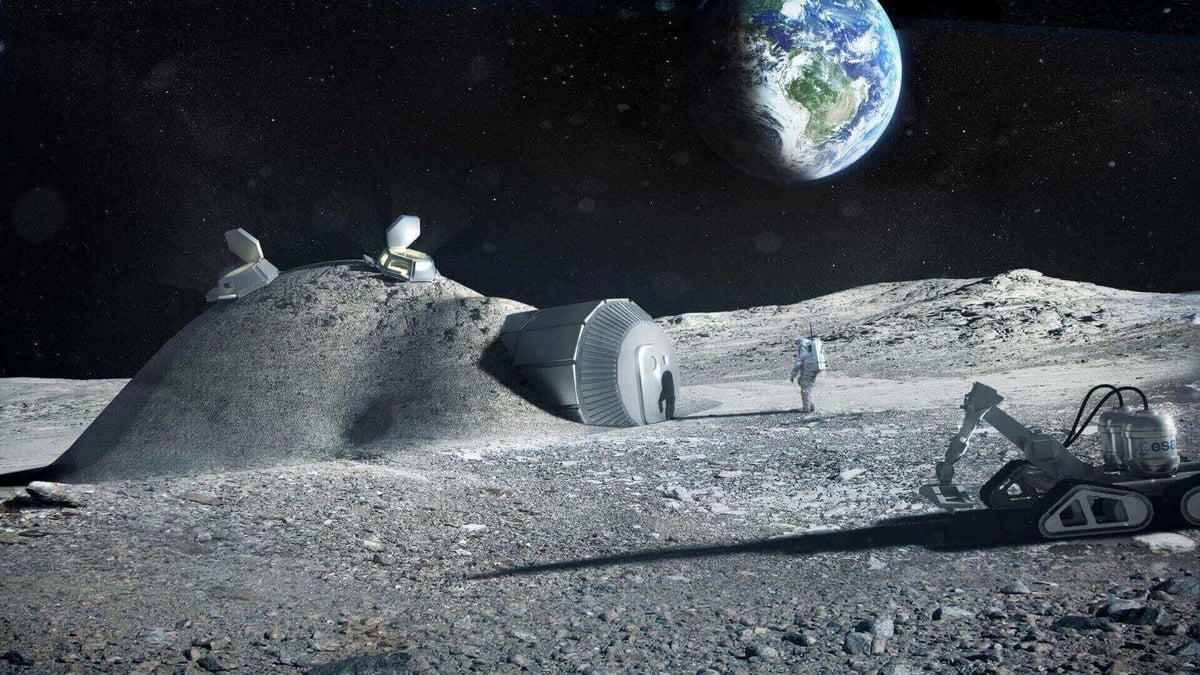

The lunar base will be 3D printed using lunar soil. A so-called D-shape printer works by laying down a thin layer of material before binding the material with a non-organic compound. This way, a whole lot of money is saved by not having to blast all the materials used in the construction of the base into space.
It may sound like an April Fools’ joke: But NASA did successfully test an almost completely 3D printed rocket engine. Although the longest of seven tests lasted only 10 seconds, the engine managed to withstand all the extreme environments inside a space rocket engine. The parts were produced using the Selective Laser Melting process: they were created by layering metal powder and fusing it using a high-precision laser.
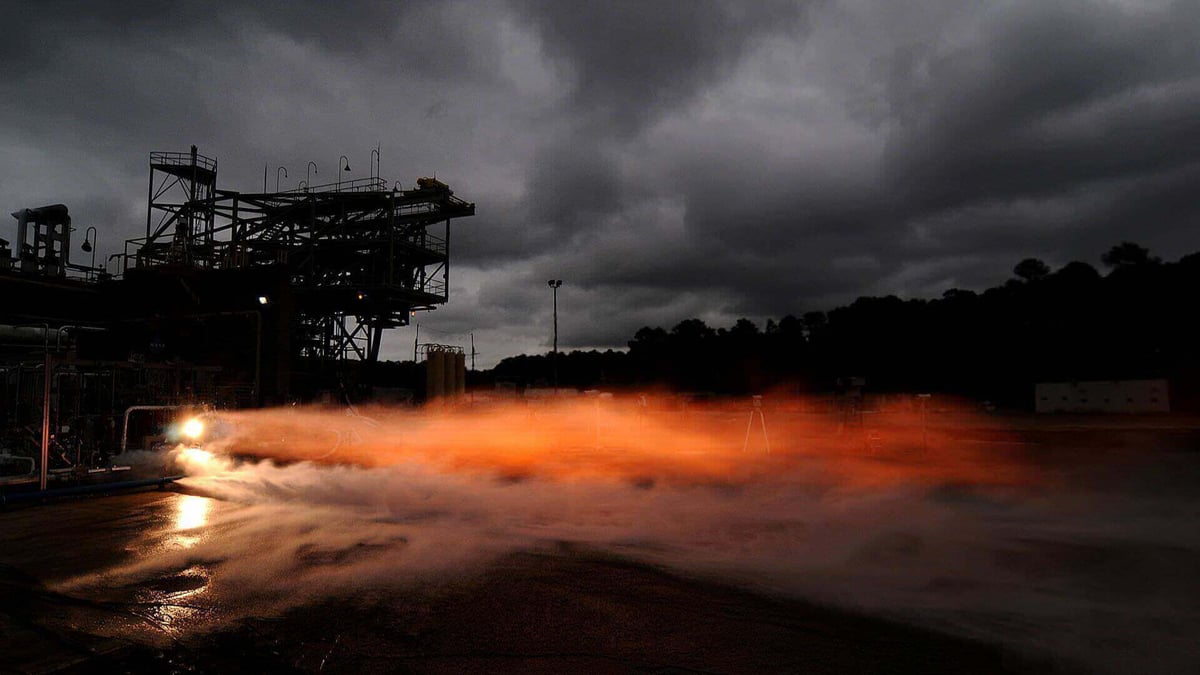

No doubt: 3D printing will definitely play a big role in future space exploration.
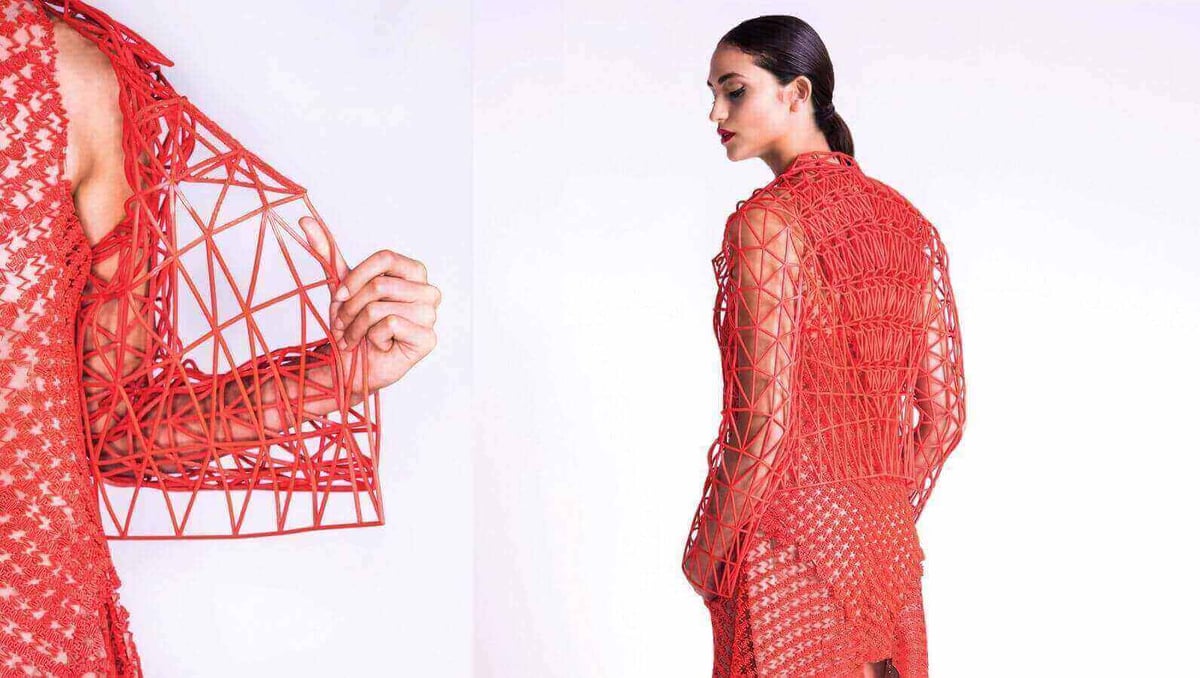
71. What is 3D printed fashion?
3D printed fashion is simply any wearable item that has been 3D printed. This includes gowns, shoes, accessories or other pieces of clothing and jewelry.
Sadly, 3D printed fashion is still expensive and time-consuming. So far, only really exists in the haute couture. Some fashion designers have been 3D printing their new designs instead of using traditional materials like cloth because 3D printing enables them to create designs never before possible. Also, 3D printed pieces of clothing are rather fragile and impractical. Yet, things might change in the future.
More on 3D printed fashion:

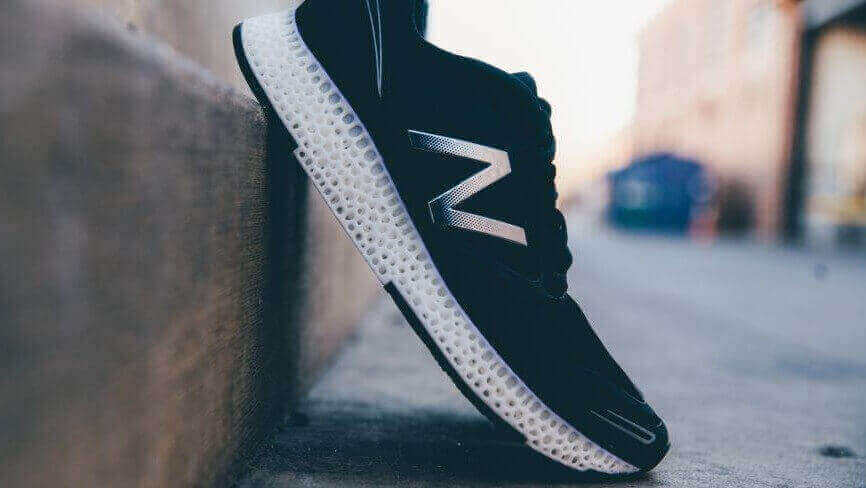
72. What are the advantages of 3D printing shoes?
Being able to 3D print a shoe allows for the shoe to be designed in a way that wouldn’t be possible using conventional methods. New Balance has partnered up with 3D Systems to create develop a 3D printed running shoe based on specialized data they have collected.
On their website, New Balance describe the advantages of the new process saying: “The new midsoles leverage the benefits of 3D printing and breakthroughs in available materials to achieve an optimal balance of flexibility, strength, weight and durability in an intricate honeycomb midsole structure.”
There are several other companies working in 3D printed shoes. More here.

73. What is the benefit of 3D printing jewelry?
Definitely it’s customization. Being able to 3D print jewelry that is based on a 3D printable model allows anyone to design their own jewelry. You don’t have to know a whole lot about working metal. The designer can either choose to 3D print their own casting molds and do everything themselves or upload the design to 3D printing service like Shapeways, i.materialise, or Sculpteo. The service will them create the jewelry for you and send it to you in the mail. 3D printing also means that multiple identical copies can be made, something not so easy to do if the jewelry is handmade. Changes to the design are also no problem. Simply modify the deign file in a 3D modeling program.
Cool 3D printed jewelry: 20 Outstanding Pieces of 3D Printed Jewelry

74. Is 3D printing food possible?
Yes. It 3D printing food is possible and is already being done. All you need to do is make the food extrudable. The food paste is then loaded into a syringe-like container and pushed through a nozzle onto a plate or build platform.
There are some drawbacks, though. Even if you can create great looking food, it’s nearly impossible to 3D print a whole meal for several people – the printers are simply not fast enough. Still, chefs are embracing the 3D printing technology very fast.
Have more questions related to 3D printed food? Here is our FAQ with the 20 essential questions and answers.
75. What kind of food can be 3D printed?
As long as your food is liquid with the suitable viscosity, you can load it into a food 3D printer. Aside from that, people have 3D printed chocolate, pureed fruits and vegetables, sugar (candy), pizza (dough first followed by the toppings), nutritional soft food for seniors and even real beef meat for hamburgers.

76. Can chocolate be 3D printed?
Yes, chocolate can be 3D printed. Perhaps even better than other foods. Since chocolate can melt, it can be pushed through a heated extruder and cooled to a solid much like thermoplastics. Unfortunately, there’s no chocolate 3D printer available on the market – but you can resort to all-in-one printers like the Zmorph.
77. Can I pimp my bicycle with 3D printing?
Yes, you can download and 3D print many bike accessories from online 3D model file sharing websites or design cool accessories yourself. Bottle holders, light mounts and tire levers are very useful accessories just to name a few.
For more info on 3D printed bike accessories click here.
And you can not only enhance a bike: Japanese company Triple Bottom Line was the first to fully 3D print a road racing bike.

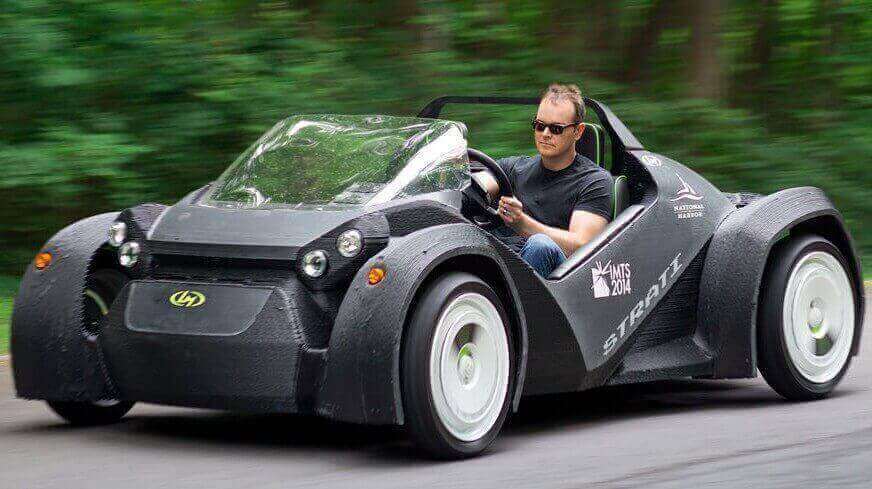
78. Do 3D printed cars really exist?
Yes, 3D printed cars really do exist. But you might be thinking of a completely 3D printed car. The problem with that, is that complex components like the engine just can’t be 3D printed (yet). Also, the wheels cannot be 3D printed yet.
The Strati is a 3D printed car that was 3D printed in just 44 hours throughout the course of the IMTS 2014 show in Chicago. The car is supposed to be 85% 3D printed parts in total with the rest being traditional components like the engine, battery, electronics, wheels etc..
The company behind this 3D printed car is Local Motors, whose goal is to revolutionize the approach to designing and manufacturing cars. If you want to know more about 3D printed cars, read on here.

79. What are the most advanced things you can do with 3D printing?
3D printing has opened up new opportunities, particularly in the fields of aerospace and medicine. Certain jet engine components with complex inner geometry can now be manufactured using 3D printing. These parts would have been near impossible to manufacture using conventional methods.
Many space exploration projects/concepts rely heavily on the use of 3D printing. For example, the Russian and European space agencies plan on 3D printing bases on the moon using moon soil instead sending all the materials from earth. This would save tons of money.
On the medical front, scientists are working on bioprinting, which would allow living tissues, bones and organs to be 3D printed/grown in a lab for transplant patients. Other advancements in medicine due to 3D printing are the design and creation of patient specific tools and objects.
80. What things are made possible only because of 3D printing?
Many things have been made possible thanks to 3D printing. Exciting advances in the medical field, varying from customizable and affordable implants and prosthetics to personalized tools and apparatuses to 3D bioprinting which is in the early stages. 3D bioprinting should be capable of growing working human organs and tissues for transplant patients.
Advances in automobile and aerospace technology have also been made possible with 3D printing. Design processes have been made a lot faster and cheaper, and even end-product components, that wouldn’t be possible otherwise, are being 3D printed.
More on this topic: 7 Things Made Possible with 3D Printing & Digital Fabrication.
81. What are the biggest things that can be 3D printed?
The largest objects to have been 3D printed are houses. The Chinese construction company HuaShang Tengda claims to have 3D printed a 400m² two-story house in just 45 days. Unlike other building companies using 3D printing, Huashang Tengda first erected the frame of the villa and then printed concrete over it using its custom-built 3D printing system (most other companies build parts such as the walls first and assemble them). The walls are 25 centimeters thick and are estimated to withstand earthquakes up to level 8 on the Richter scale.

More on 3D printed houses in this article.
82. What is the biggest thing which was 3D printed?
The current Guinness World Record holder of the title “Largest 3-D printed object” is the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL). They have 3D printed a tool that will be used in the production of the Boeing 777X, a new and improved version of the popular and successful Boeing 777 airplane. The object is 17.5 feet long, 5.5 feet wide and 1.5 feet tall. According to the definition of the record title the object is solid.
83. What is the smallest thing which was 3D printed?
Dr. Timo Gissibl along with his colleagues at the University of Stuttgart in Germany were able to 3D print a tiny camera lens onto the end of an optic fiber. The whole lens is thinner than a human hair. The researchers involved in this project have said that this new technology could revolutionize surgery, create better endoscopes and even aid autonomous machines like robots and drones.
For more info on this topic, click here.
Also, Artist Jonty Hurwitz has 3D printed the smallest sculptures using photopolymer materials and light. The artwork is stunningly beautiful when seen under the microscope, which you need because some of the sculptures are smaller than half the width of a hair and portray amazing detail.
3D Printing Guide: The Industry
No doubt: 3D printing is about to become a leading industry in the future. What is the state of the industry today – and what can we expect in the future?
84. Which are the fields of industrial 3D printing?
3D printing is being used in the aerospace, automobile, medical, architecture, consumer goods/electronics, defense, and education industry.
Since there are many situations in which 3D printing is cost efficient, 3D printing has found its place in many industries. Think of the time saved by 3D printing an architectural model as opposed to constructing or milling one.
85. How to invest in 3D printing stocks?
Here is a 4-piece series on investing in 3D printing stock (Part 1, Part 2, Part 3, Part 4).
And here is another article on this topic:
86. Which 3D printing companies are trustworthy?
3D printing companies are no different than other companies when it comes to trustworthiness. The same precautions should be taken when looking into using a 3D printing company’s services as with any other company. To be safe, use Google to do some research on the company and look for customer experiences and reviews.
These 3D printing companies are beyond doubt: The Best Online 3D Printing Services in 2024
87. What impact will 3D printing have on the economy?
On-demand manufacturing and mass customization will have tremendous effects on our economies. Here is a detailed article on this subject: How 3D Printing Will Change The World.
Apart from impacting the economy, 3D printing will also have effects on the taxation system. One of the major issues is deciding on whether the value of a product lies in its physical state or in its digital design. This is an important question, as 3D printing permits localized manufacturing.
More on the topic of 3D printing and taxes: 3D Printing Will Turn Tax System Upside Down.
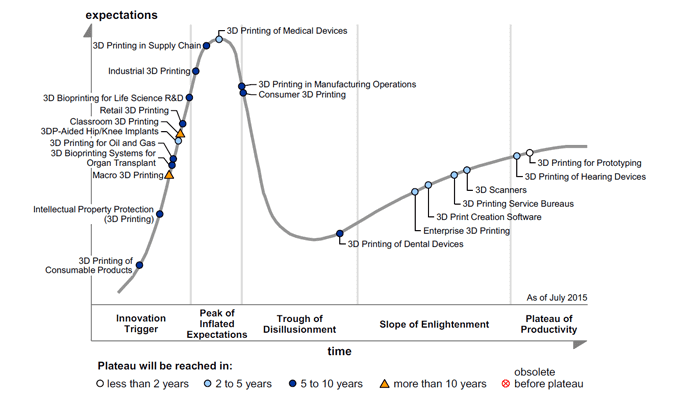
88. Where is 3D printing on the Gartner hype curve?
The hype cycle visualizes the growth curve of emerging technologies. As it turns out, 3D printing can be divided into very many subcategories, some more mature than others.
Current research done by Gartner shows that 3D printing for prototyping and hearing devices are already entering the plateau stage, whereas 3D Printing in manufacturing operations is currently in the so-called trough. At the very peak of the curve are stereolithography and 3D printing of medical devices for example. On the rise to the top are 3D bioprinted organ transplants and intellectual property protection in 3D printing.
More on the Gartner hype curve and 3D printing: Gartner’s 3D Printing Hype Curve: The Best is Yet to Come.
89. How big is the 3D printing industry?
According to statista, the 3D printing market is worth 7 billion USD in 2016 and is estimated to reach 21 billion USD by 2020.
90. Will 3D printing change the world?
Many believe that 3D printing will indeed have a major impact on the world of manufacturing. Decentralized and local manufacturing combined with mass customization will certainly change the products are designed and manufactured along with the logistics of the processes. More on how 3D printing could change the world.
3D Printing Guide: 3D Printing Services
91. Do I need a 3D printer for 3D printing?
No. You can 3D print without a 3D printer. If you have an idea, or you designed a 3D model but don’t own a 3D printer, then it’s not the end of the world: There are a number of 3D printing services out there that that will be more than happy to 3D print your model.
The three big services are i.Materialise, Sculpteo, and Shapeways. They allow you to upload an STL file and have it 3D printed in high quality and even in premium materials like precious metals. You also have the option to select an object from their website to save yourself the 3D modeling. Even better: Use All3DP’s price comparison service – in this case, you upload a 3D model, get quotes from i.Materialise, Sculpteo, and Shapeways with a few mouse clicks and directly place your order.
Apart from “the big three”, there are other services either by companies or based on the 3D printing community. This means that private individuals or companies can offer 3D printing services through an online platform like 3D Hubs or MakeXYZ. This way, you can have someone in your region 3D print your model and deliver it (or you can pick it up) for a certain upon price. More on that in our overview of online 3D printing services.
92. Which is the best 3D printing service for my purposes?
If you are looking for an easy hands-off experience, then choose one of the major online 3D printing services: Shapeways, i.Materialise or Sculpteo. These services also let you sell prints of your design. The service prints and delivers your design. All you have to do is create the 3D model.
If you are looking for a more hands-on experience, but still don’t want to buy your own equipment, then look up the nearest Fab Lab. Fab Labs offers you the use of a range of 3D printing equipment and other manufacturing machines in exchange for a small fee. This way you can still 3D print your models by yourself without the need for your own 3D printer.
For more on this topic: Here is our overview of the most important printing services.
93. Where can I find a 3D printing store?
3D printing stores are located in larger cities like New York, Amsterdam, and Berlin. They sell 3D printed goods and some even offer 3D printing services with industrial-grade 3D printers.
The first 3D printing store is located in Amsterdam and is called “Printed in Space”. The owner of the shop started out selling 3D printed objects from a Ultimaker printer.
For more on this topic: The Best 3D Printing Stores in Europe.
94. How can I get something 3D printed in full color?
You can have objects 3D printed in full color at a variety of 3D printing services, the most popular being Shapeways, i.Materialise and Sculpteo. The largest industrial full-color 3D printing service in the world is whiteclouds.
There are 3D printers on the market that do full-color 3D printing but they are still very expensive. Other processes like computational hydrographic printing use a special coloring technique which is a cost-effective, post printing alternative to other methods.
More on hydrographic coloring: Hydrographic Printing: Affordable Full-Color Prints for Everyone.
95. What is a 3D printing service bureau?
A 3D printing service bureau is a local business or outlet that will handle anything 3D printing for you. If you want something designed, you can ask your local 3D printing service bureau. If you want that design 3D printed as well, you can have your 3D printing service bureau do that for you. They will often also offer a 3D scanning service. Using a 3D printing service bureau can be very cost effective for your needs. It depends on how often you would like to do 3D printing.
96. Who can 3D print parts for medicine?
Any company or organization may 3D print medical devices. However, any medical devices both manufactured in the USA or imported from outside the USA must be approved by the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration).
97. How can I find a 3D printing service for my business problem?
Giants like Stratasys, EOS and 3D Systems both offer professional and industrial 3D printing solutions for businesses.
98. Where can I buy things made with 3D printing?
3D printed things can be purchased almost in a lot of places. First of all, many major cities have 3D printing stores where you can buy 3D printed objects and even 3D printers. Perhaps the most popular place to buy 3D printed things is through an online service. These services let you upload an STL file and have it printed and delivered. Many other similar services exist.
Also, ALL3DP offers a 3D printing price comparison service that makes uploading your file and selecting the material and printing service a snap.
99. Who can make a 3D selfie and 3D print it for me?
There are a lot of local services offering 3D selfies – a Google search will help you with that. One of the most popular 3D selfie services, the DOOB Group, offers 3D printing and scanning services in major cities like Berlin and New York.
- 3D Selfies: Enter to the Photo Studios of the 21st Century
- 5 things you should know before you buy a 3D Selfie
- More than 3D selfie studios: The Doob Group
3D Printing Guide: 3D Printing as a Business
100. How can I make money with 3D printing?
There are many ways to make money with 3D printing. If you have a 3D printer, why not make money 3D printing things for other people while you’re not printing for yourself. Services like 3D Hubs are there for that exact purpose.
Another way to make money is to design 3D models for money. Use your creative and modeling skills to make money with it. Online services like Shapeways allow you to sell your designs. The service 3D prints the model when someone orders it and you, the designer, get a portion of the price of the object. There is a number of comparable services.
More on how to make money with 3D printing Networks and Products.
101. What is the best way to sell 3D printed things via the Internet?
The best way to sell 3D printed things on the internet is a place where people look to buy 3D printed items. Popular platforms include Etsy (jewelry and art), Shapeways, i.Materialise and Sculpteo. 3D designers use these platforms to sell their 3D printed creations.
The advantage of Etsy is that the designer is responsible for having the product made. This way, the entire end product can be shipped with all its accessories. Shapeways, on the other hand, ships the raw 3D printed object directly to the buyer without accessories.
More on this topic: Sell Your 3D Printed Items On Etsy, Amazon and eBay.
License: The text of "The Ultimate 3D Printing Guide (101 Questions Answered)" by All3DP is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
