A Strong & Growing Industry
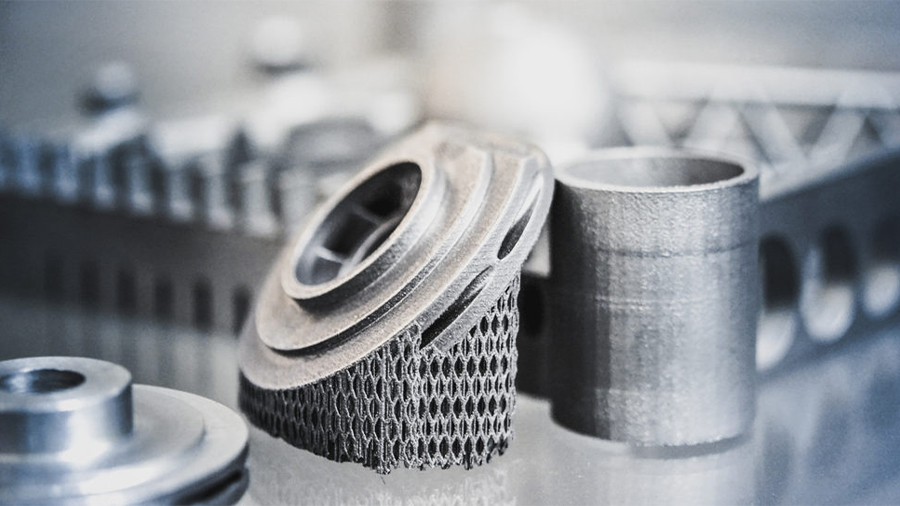

3D printing has come a long way since its advent back in the 80s. Once referred to as “rapid prototyping” and intended for that purpose, 3D printing technologies have matured to a state where many other applications are suitable, including end-part production.
Known today as 3D printing or additive manufacturing, these technologies exist in a fast-changing environment, where new processes, equipment, and applications are being developed as each day passes. Although 3D printing won’t completely replace traditional manufacturing techniques, it has proven its strengths and is already revolutionizing many industrial sectors.
In this article, we’ll discuss the top 10 advantages of 3D printing in 2020 and give some real-life examples of how these marvelous technologies are being used every day.
Accessibility
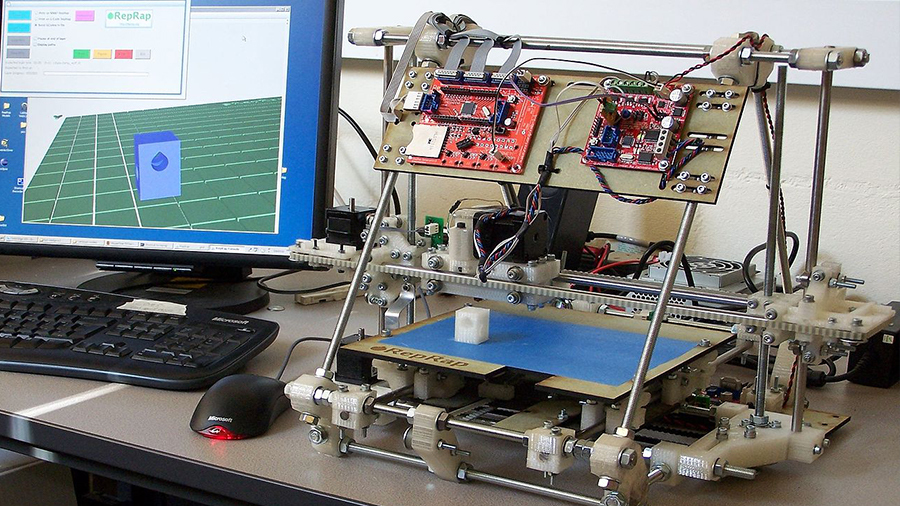
Before diving into the more distinct advantages of these technologies, let’s look at a broader aspect of 3D printing that’s arguably the most significant of all: accessibility. This is a relevant factor in a couple of the advantages in our list, so we’ll start with some context.
Although 3D printing technologies were first developed in the 1980s, not a lot happened over the subsequent 20 years, as high costs and strict patent restrictions limited their use to mostly high-end industrial applications. During this time, these infant 3D printing technologies evolved at a rather slow pace.
That started to change with the RepRap project in 2005, founded by a couple of academics in the UK. The idea was to develop low-cost 3D printers with open-source designs so that anyone could build one. This was a huge step towards accessibility and eventually set off a new age in 3D printing.
Open-source development and greater accessibility provided the push required not only to popularize the technology but also to promote further development in the area. Fast-forward to today and there are countless 3D printer manufacturers and companies, and virtually anyone can 3D print an object, whether at home or via shops and online services.
With all of that said, it becomes clear that accessibility has been a core part of the growth of 3D printing, as well as one of its main advantages overall. In fact, the first three advantages on our list are all related to access. Let’s jump in!
Accessible Equipment
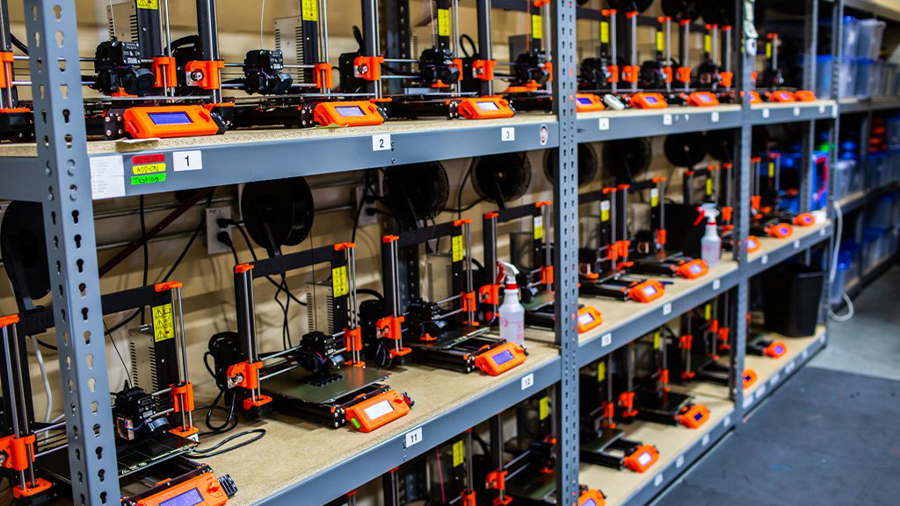

All in all, it was accessible equipment that significantly put 3D printing on the world map. How many 3D printing companies, material suppliers, and spare-parts manufacturers were born out of the popularization of desktop 3D printing?
Today, there’s a 3D printer for everyone: different sizes, prices, technologies, you name it. Moreover, there are hundreds of detailed open-source designs online that, allied with numerous suppliers worldwide, allow anyone to plan and build a 3D printer from scratch at a very low-cost.
Whether bought or built, desktop 3D printers are fairly easy to use, which further enhances accessibility. The workflow required to process and print an object is relatively straightforward when compared to other digital fabrication techniques such as CNC routing or milling.
Then there’s the other side of accessibility: the cost. Back in the early 90s, an SLA 3D printer used to cost around $300,000 (around $600,000 in today’s figures). 20 years later, in 2010, the average cost of a 3D printer ranged around $50,000, which was still far too expensive for most home users.
These days, depending on your use case, desktop resin printers range between a couple hundred and a few thousand dollars. At the affordable end of the scale, DLP machines like the Elegoo Mars and the Anycubic Photon cost around $200 apiece, while two of the most popular FDM printers, the Original Prusa i3 and the Creality Ender 3, currently cost around $750 and $200, respectively.
The huge variety of desktop printers intended for at-home use and the vast drop in price in recent years just goes to show how accessible 3D printing has become.
Accessible Production

We’re well past the age of corporations and big factories holding all the manufacturing resources. Owning a manufacturing machine allows individuals to produce their own goods anywhere. This is true of most digital fabrication equipment, but especially 3D printers as they are generally small and easy to setup.
Add that to the ever-growing demand for digital modeling and you can see the entire production process shifting towards the people. This sparked the creation of many small manufacturing businesses that were previously only possible with artisanry skills and high investments in physical space and equipment.
This democratization of production has empowered the user, with many hobbyist-level makers now fixing and creating their own stuff rather than simply replacing and buying new. While many industrialists feel threatened by this, some have decided to join the movement.
One example is camera equipment company Edelkrone, which has a line of products known as Ortak manufactured by both the company and the customer. Edelkrone produces and ships the critical parts such as metal joints and electronic components while providing the customer digital models for 3D printing the remaining parts of the product. Not only does this reduce prices, but the process allows customers to customize designs as they please.
Custom jewelry company Radian is yet another example of how 3D printing can be applied for local production. The Berlin-based company produces stunning rings, necklaces, and bracelets using 3D printing in mainly two ways: either by lost wax casting methods or directly manufacturing via powder bed fusion processes.
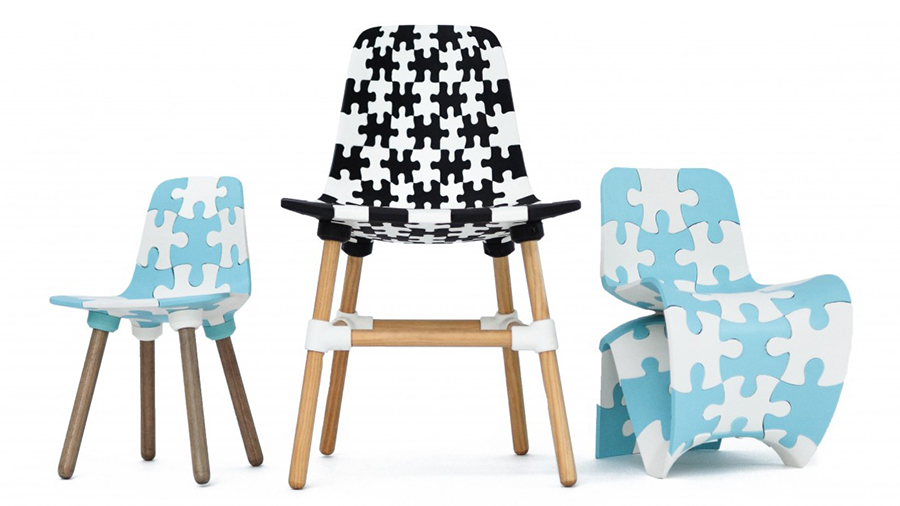
Before we move on to the next section, the Bits & Parts project also deserves a brief mention here. It allows anyone with an FDM printer to 3D print cool chairs almost entirely. The Maker Puzzle Chair models can be downloaded for free and are composed of several small parts designed to fit most home printers.
Open Community

All the accessibility in both production and equipment would just not be possible without the open-source design practices initiated by the RepRap community. The rebirth of 3D printing was based on open-source principles for both hardware and software.
The term “open source” is borrowed from software development models in cases when the code is open to anyone to see, use, and, most importantly, enhance. This enables worldwide cooperation among users with different backgrounds and talents.
3D printing today is still in great part open source. Companies like E3D, Prusa Research, and Lulzbot share their hardware drawings and models with anyone, while open-source software options include Marlin firmware and the ever-popular OctoPrint.
This mindset is also extended to 3D models. Platforms like Thingiverse, Cults, and MyMiniFactory have thousands of free models to download that are shared among 3D printing users.
Last but definitely not least, an open-source community has promoted the creation of many unofficial support channels and educational online resources that have saved many of us when we’ve run into trouble with a print.
Short Lead Times & Rapid Iteration

There’s a reason why 3D printing technologies were once referred to as “rapid prototyping”. The short amount of time required between creating and manufacturing a part makes this technology perfect for rapid design iterations.
This is especially relevant during product development, where the product requires several validations from concept to final functional testing. Since 3D printing doesn’t require any special tooling and setup for producing parts, all that’s required is to modify the digital model and send it off to the 3D printer.
Rapid iteration reduces the costs associated with producing prototypes and shortens the development process, allowing the product to reach the market faster than ever. The ability to easily iterate between different designs also makes for a better product as the development team can verify and test proposed changes in a fast and cheap manner.
The automotive industry has been leveraging this advantage of 3D printing for quite some time now. For example, the engineering team at Ford relied on 3D printing for prototyping parts for the new Shelby GT500. Performance engineer Matt Titus claims this technology “improves the effectiveness of the designs, it dramatically reduced the time it took to develop the GT500 – and the costs associated with that.”
However, rapid iteration is not restricted to big corporates like Ford. The humble desktop 3D printer user also greatly benefits from this advantage. Creating your own parts for whatever end can be a daunting task for some and the ability to easily modify and re-print your designs is definitely the recipe for success.
Geometric Freedom
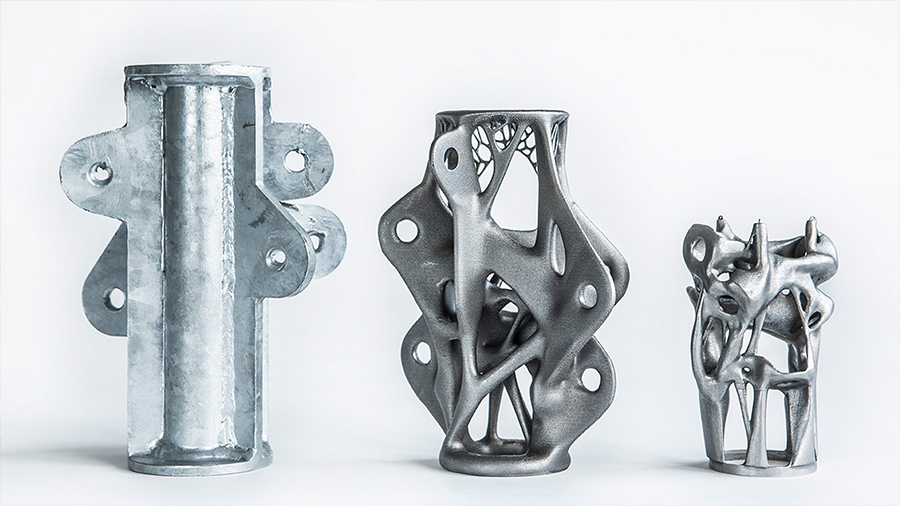

One of the core advantages of 3D printing is the ability to create physical shapes and features that otherwise would be impossible to produce using traditional manufacturing techniques.
The layer-by-layer fabrication method provides such geometric freedom that designers and engineers today are not yet able to take full advantage of. The traditional way of designing parts and products was guided by very restrictive manufacturing methods such as milling, forging, and molding. To truly leverage this unparalleled freedom of creation, engineers must really think outside the box.
One example of this is GE’s jet engine fuel nozzle tip, an assembly that was completely redesigned taking into account all design allowances provided by their metal 3D printers. In the end, the 20 parts that made up the nozzle tip were replaced by a single 3D printed part that was 25% lighter than the former.
Another example where geometric freedom was the star of the show is the NightHawk headphones by AudioQuest. The headphones feature a 3D printed grille that mimics the structural pattern of butterfly wings to diffuse sound and enhance acoustic isolation. Product director Skylar Gray claims the intricate NightHawk’s grille design was not possible to be manufactured five years ago: “The only way it could be created is through today’s advanced 3D printing.”
Materials

Some may say 3D printing is only as useful as the materials it can process. This is arguably true, since most functional products on the market require a certain level of quality control to comply with local regulations. This is why the technological advances in 3D printing go hand-in-hand with material development.
Metal 3D printing is now quite common, being able to process high-end titanium alloys for very strict industries such as aerospace and medical implants. Ceramics have also become a popular material for 3D printing, not to mention all the advanced polymers widely available.
For the home user, there is a wide range of materials that can be processed by a desktop 3D printer, including metal-infused plastics and even carbon fiber filament. The worldwide network of materials suppliers is huge, ranging from small local manufacturers to big companies like eSun.
Some very high-performance plastics can be 3D printed by desktop FDM machines with hardware tweaking. That’s the case for PEEK, a polymer so resistant to wear and heat that it can replace metals in some industrial applications. While it requires very high temperatures for printing (around 400 °C), it’s not something totally unachievable as certain hot ends are developed specifically to withstand such temperatures.
For SLA, one example of specialized materials is the biocompatible resins used for dental applications. These are usually commercialized by 3D printer hardware manufacturers like Formlabs and Zortrax, but there has been a recent growth in third-party competitors such as NextDent.
Customization & Personalization
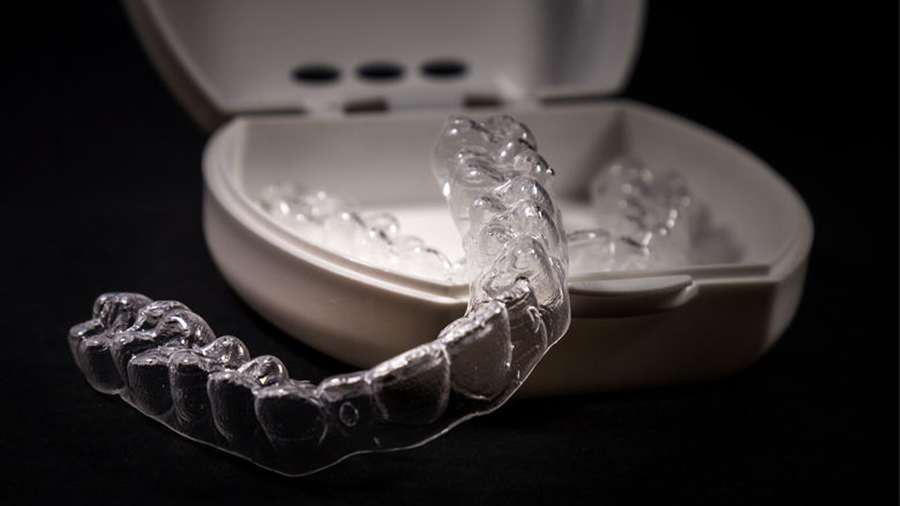
The customization provided by 3D printing is definitely one of the top advantages of this technology. As previously mentioned, the lack of necessity for special tooling to produce parts is what enables a single design to be changed and produced quickly.
This flexibility also allows for viable mass-customization production, where personalized products can be produced while maintaining the low costs associated with mass production. This is a potential game-changer for many industries and should also provide better products for customers to reach the market.
Some products that rely on personalization have been using 3D printing processes for a while now. For example, Invisalign produces over 320,000 clear aligners every day using 3D printed molds developed from the patient’s 3D scanned mouth.
But thinking in a more local environment, 3D printer owners are able to design and print custom parts for everyday items such as personalized car accessories, or custom-made replacement parts for home appliances and even old furniture.
Economic Viability
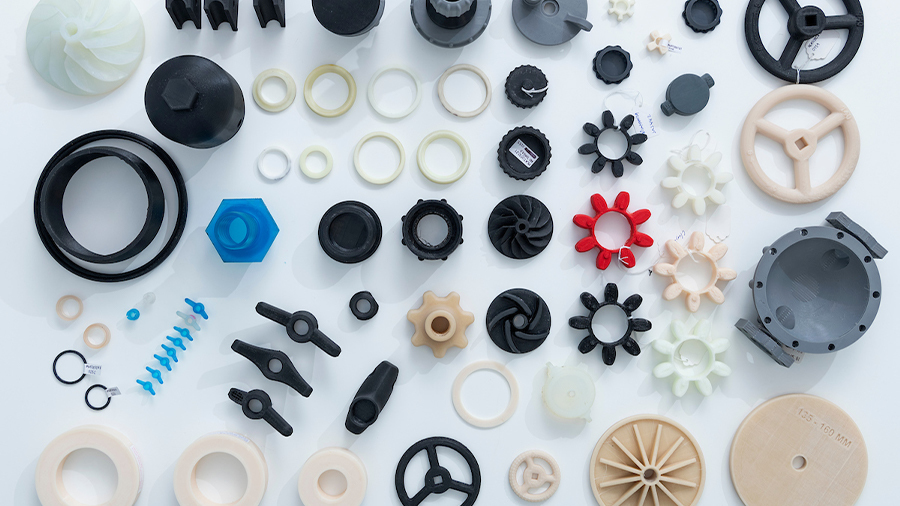

The production flexibility associated with 3D printing provides economic viability for many business models that otherwise would have been impossible to implement, including the already-discussed mass-customization of products.
The digital workflow and rapid design iterations make medium-to-low-batch production feasible for many industries. Specialized products like limited editions and low-demand items can be produced at low-costs with 3D printing, opening up many possibilities in different commercial sectors.
3D printing technologies provide even further economic gains if outsourced parts and tools start being produced in-house. Furthermore, flexible manufacturing systems have smaller inventory requirements, especially considering the shorter lead times provided by 3D printing.
On-demand production for both goods and spare parts will become the norm for some industries in the near future, but that doesn’t mean a few companies haven’t started already. Rather than keeping an endless inventory of parts for its classic cars, German sport’s car manufacturer Porsche has been 3D printing them. Not only is it cheaper for Porsche, but many classic car collectors can now source parts directly from the manufacturer instead of trawling the world for hard-to-find parts.
Reduced Waste
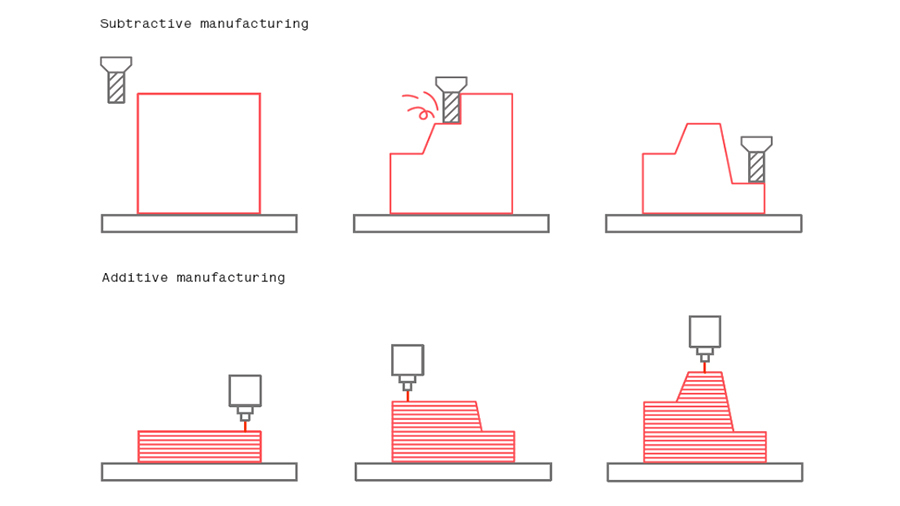
Fabrication techniques such as CNC machining became known as subtractive manufacturing, as opposed to additive manufacturing where the parts are built by adding material layer-by-layer. Subtractive manufacturing has inherent waste as the final geometry is only achieved by removing material from the “stock”.
Depending on the complexity of the part, only a small fraction of the stock material will eventually become the part or product, with the rest being wasted as recycling options are uncommon. On the contrary, the losses associated with 3D printing are minimal, often related to support structures.
Computer optimization techniques like topology optimization and generative design allow engineers to design better-performing parts with less material. In practical terms, a redesigned part can be even stronger than a previous model, even while consuming less material.
While the optimized geometries are awfully complex, they are now possible to manufacture thanks to 3D printing. Some companies like aircraft manufacturers have a special interest in this, as weight reduction translates into direct fuel savings for airplanes.
Thanks to metal 3D printing processes, Airbus has recently developed an optimized cabin partition for its A320 aircraft family that weighted almost half of the original. Moreover, the high-end metal alloys required for aircraft production are quite costly to be wasted in subtractive processes.
Broad Range of Applications
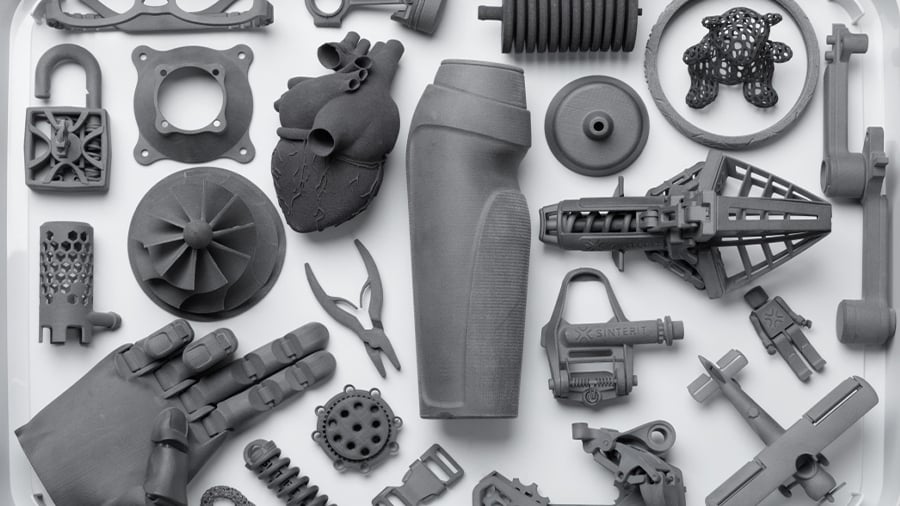

By now it should be more than clear how 3D printing has gained terrain across many industries worldwide. All the advantages already mentioned in this article contribute to this broad range of applications that’s only expanding.
The accessibility and flexibility provided by 3D printing processes were often mentioned throughout this article, being perhaps the traits that mostly stand out from the other manufacturing processes the industry is used to. Mainly because of such traits 3D printing technologies are so diversely applied in sectors ranging from health to aircraft production.
The fact that there are many different 3D printing techniques also contributes to this wide range of applications. With SLA for jewelry and dental, SLS and SLM for engineering, and the good old FDM known and loved by so many hobbyists today. The possibilities are endless and the future looks brighter than ever for 3D printing.
Lead image source: David McNally via US Army
License: The text of "The Top 10 Advantages of 3D Printing" by All3DP is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.





