If you’re not familiar with the term, “5D printing” would be more accurately called “5-axis printing”, as you’re actually printing using five axes rather than adding more dimensions to the print. Standard 3D printers use three linear axes: X, Y, and Z. But 5-axis printers additionally allow for rotation in the X- and Y-axes so that curved layers can be printed.
This means complex models can be printed more easily, using fewer supports. It can also mean less material used, stronger models, higher-quality surfaces, and less post-processing!
Ready to learn more? Let’s dive in!
3D vs. 4D vs. 5D
Before we deep-dive into 5-axis (or 5D) printing, it’s worth clarifying how this is different to 3D or even 4D printing.
Just note that we’re discussing approaches to filament (FDM) printing here, not resin-based or another type of printing.
3D Printing
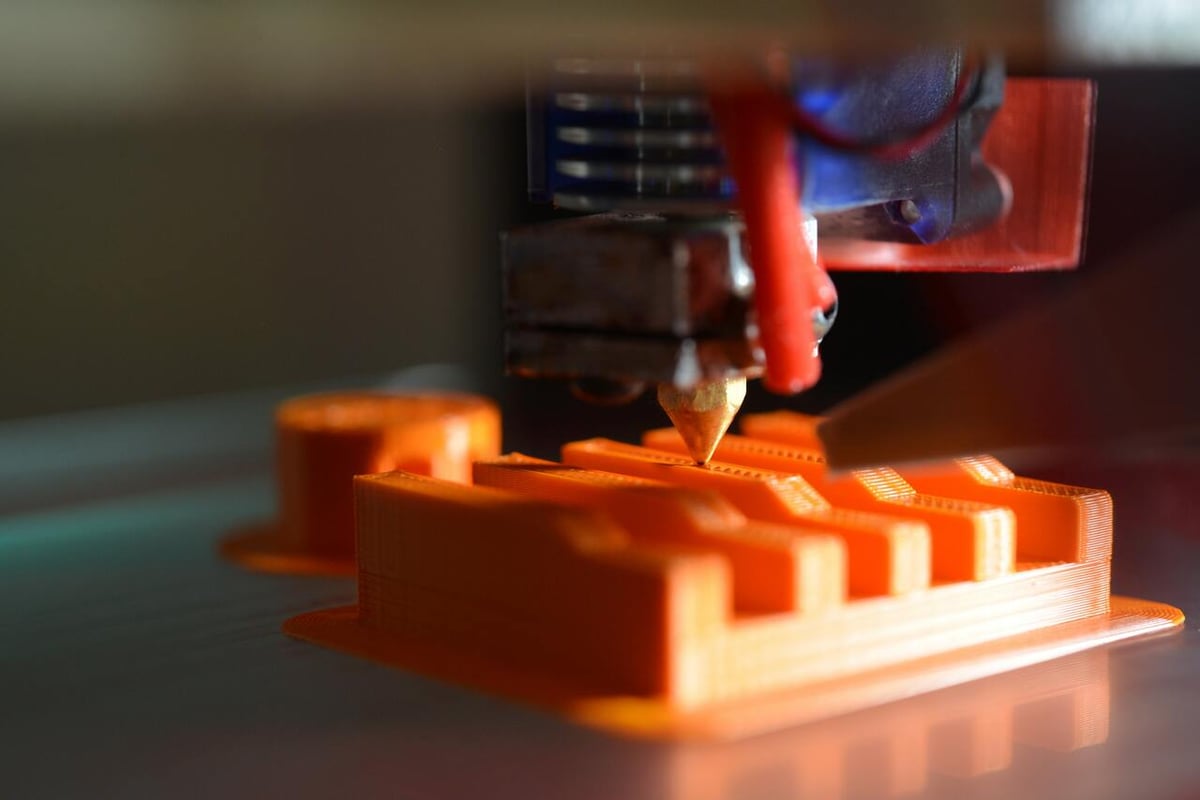
This is the most common approach to FDM printing and also the most accessible, with many desktop machines available for hobbyists. Yet, what is typically called 3D printing could in fact be thought of as “2.5D printing” as only the X- and Y-axes move simultaneously (in most cases).
The printhead moves across the XY-plane as each flat layer of plastic is printed. However, the Z-axis is only really used to “step up” to the next layer, but not while actively printing (except to compensate bed flatness or perform special travel moves).
Actually, there is a way to take advantage of the Z-axis in conjunction with the X- and Y-axes using a technique called non-planar printing, which some call “true 3D printing”.
Non-planar printing isn’t very common, as it requires a specialized printhead and specific software and is somewhat limited in it’s applications too!
4D Printing
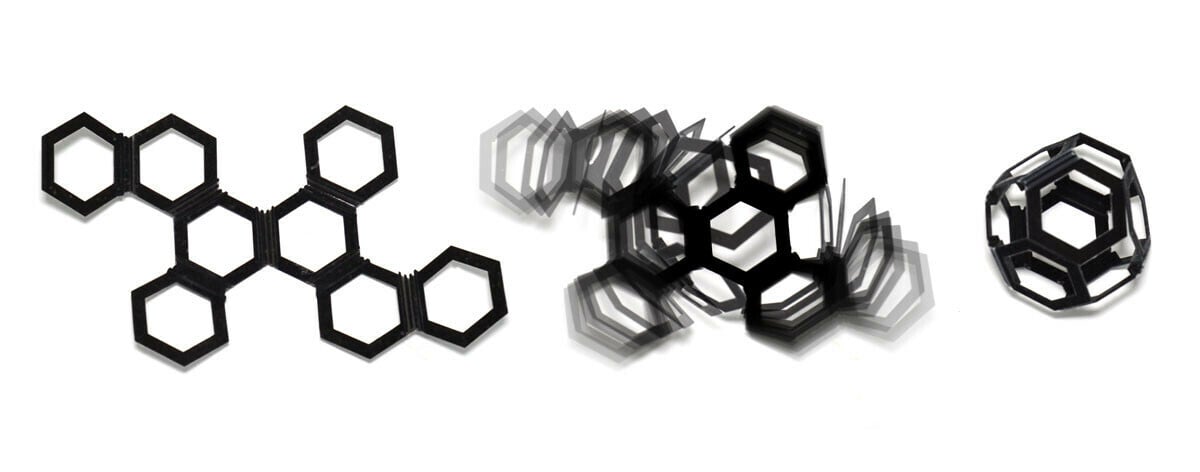

Surprisingly, 4D printing is completely unrelated to the other types of printing discussed here. (Some 4-axis printers do exist, but there’s not a lot for support for them, so they’re pretty rare. There are, however, 4-axis CNC machines.)
4D printing refers to a very different process, where traditional 3D printing methods are used to produce a model using materials or designs that will react or change shape when triggered after printing. In other words, unlike 5D printing, 4D printing actually adds the 4th dimension: time.
For example, the model may change shape when exposed to water or heat.
5D Printing
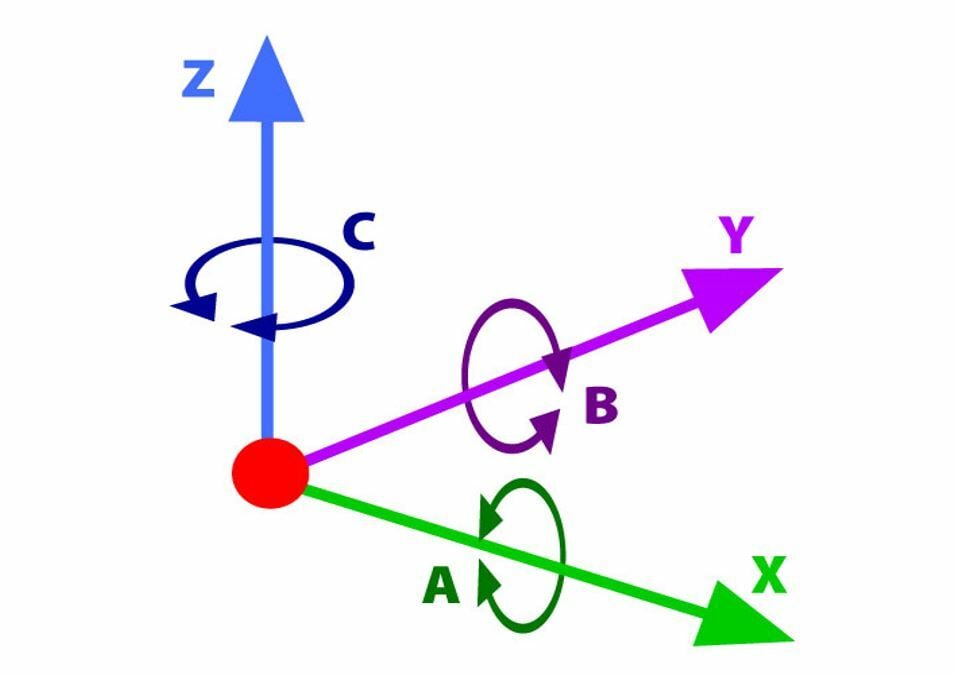
Once again, 5D printing is more accurately referred to as 5-axis printing, as you’re not really adding more dimensions but taking advantage of more axes!
If you’re familiar with CNC machines, you may have already heard of 5-axis CNC machines. Indeed, while fairly new to additive manufacturing, it’s a widely used approach in subtractive manufacturing and has been for some time.
Unlike standard 3D printers, which only use the X-, Y-, and Z-axes, 5-axis printers use 2 more:
- A: Rotation in the X-axis.
- B: Rotation in the Y-axis.
6-axis printers, which take advantage of the “C-axis” – rotation in the Z-axis – also exist. Like 4-axis printers, though, these are fairly rare.
How It Works
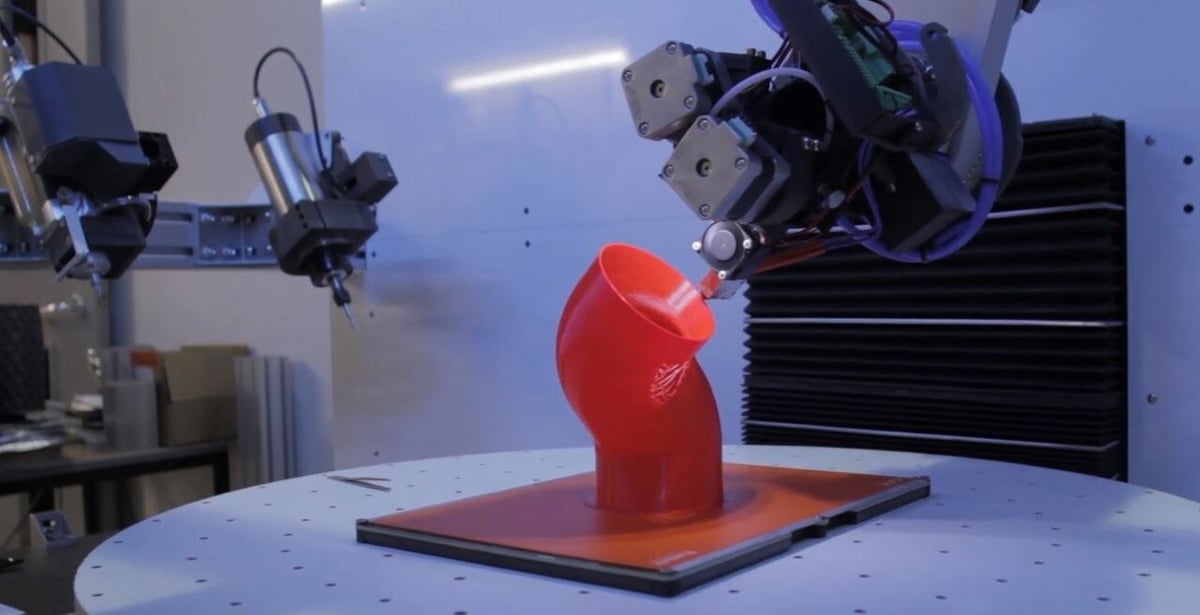
As we just discussed, 5-axis machines are fairly new within the world of additive manufacturing but are nothing new to the CNC world. As a result, many 5-axis printers are actually just CNC machines with changeable toolheads, allowing you to swap in a printhead.
Purpose-built 5-axis printers are rarer still. Many are in the research phase, where various approaches are being taken to 3D print using the five axes.
Some machines work by rotating the printhead itself in the additional two axes, with the model and print bed remaining stationary as material is deposited. Others rotate the printed bed (and therefore print itself) in the A- and B-axes instead.
By allowing for movement in these additional axes, non-planar curved layers can be printed, unlike traditional 3D printing, which is limited to printing with flat layers.
Advantages
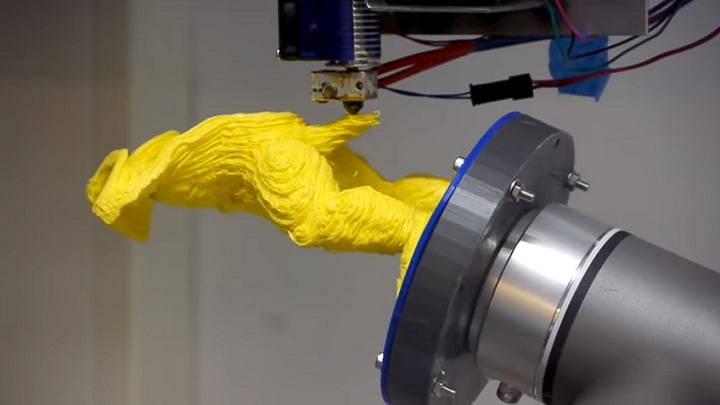

5-axis printing has many advantages over traditional 3D printing. Let’s break them down!
- Fewer supports: Thanks to being able to rotate the printhead or bed in the A- and B-axes, you can ensure the printer is almost always printing on a solid part of the model, eliminating the need for excessive supports and enabling more intricate and complex models to be printed, where supports would’ve otherwise been impossible to remove.
- Stronger prints: Standard 3D prints are always weakest across their layer lines. With 5-axis printing, you’re not limited to stacking flat layers in the same way and so can produce much stronger prints.
- Less material used: Being able to print at a variety of angles reduces the need for infill and supports, so the amount of material used can be dramatically reduced.
- Less post-processing: By not needing so many supports and not being limited to flat layers, it’s possible to produce much smoother, higher-quality prints with less need for post-processing.
Note that these advantages are only really applicable for complex models. You’re not going to gain much printing a calibration cat on a 5-axis printer.
Disadvantages
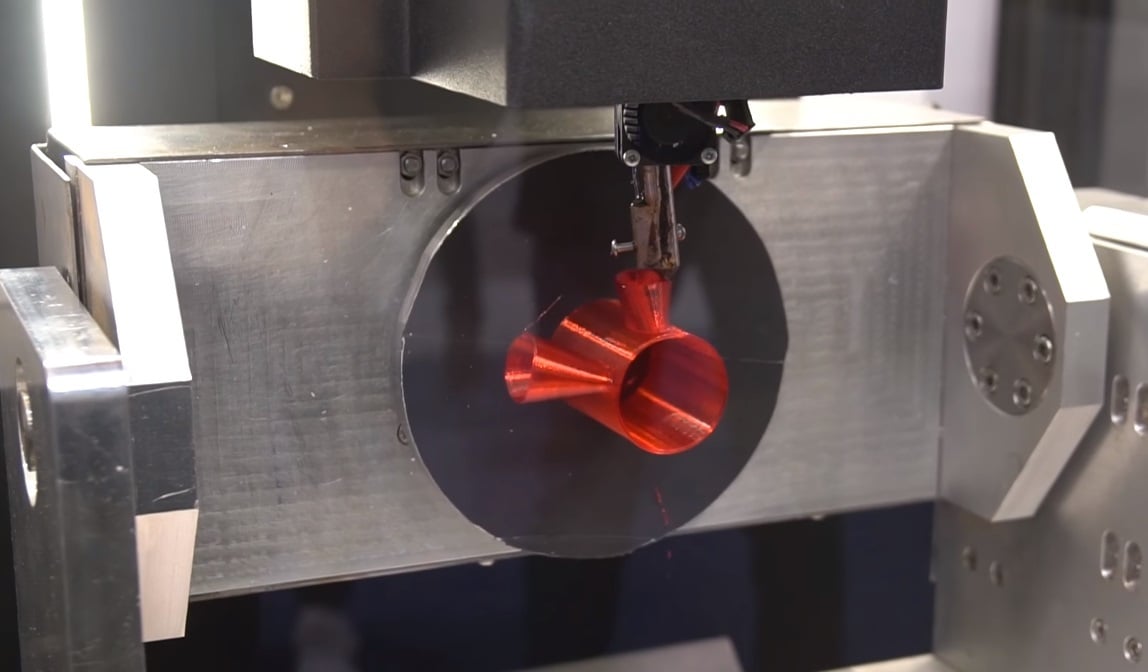
As always, there are a few downsides, too! But know that every disadvantage of 5-axis printers can be boiled down to one key issue: They’re just very, very new.
With that in mind, we can hope that these disadvantages may become less and less relevant as research continues and 5-axis machines gain popularity.
- Few options: There aren’t a whole lot of options out there, and the options that do exist tend to be intended for industrial use or are pretty expensive, making 5-axis printing fairly inaccessible for most.
- Limited support: There’s also very limited support available for these printers compared with something like standard 3D printing, where there are huge communities of users. This is obviously something that should simply come with time, but right now, you’re looking at a pretty independent learning experience.
- Complex slicing: Creating and slicing models for 5-axis printing can be hard work! 5-axis printing requires a very different approach, so you’ll likely have some habits to break when it comes to designing or selecting models to print. Furthermore, most slicers don’t even support non-planar (true 3D) printing, never mind 5-axis printing! In other words, if you want to slice a model to be printed using a 5-axis machine, you’re looking at very limited and mostly paid options, along with a fairly steep learning curve.
Applications
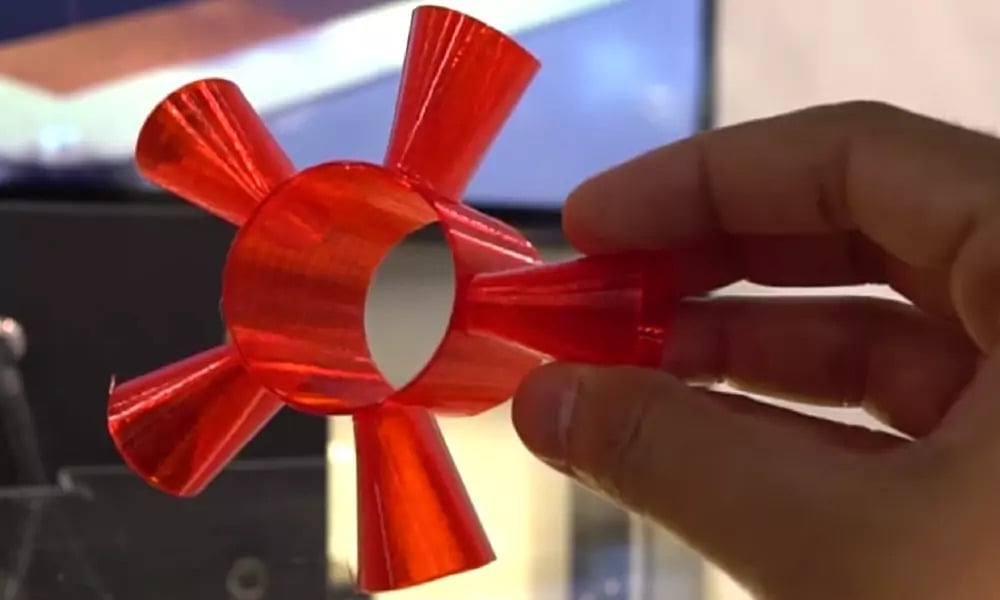

Due to the discussed advantages and disadvantages of 5-axis printing, applications are currently mostly limited to those sectors where the advantages are really worth the additional costs over other forms of manufacturing. As such, it’s mostly used for industrial applications right now.
5-axis printing is an ideal technology to be used in industries such as the aerospace or automotive industries, where the strength and accuracy of parts are absolutely essential.
Many medical fields, such as dentistry, orthopedics, and prosthetics take advantage of 5-axis printing, too, meaning that custom and often complex models can be manufactured to fit the patient comfortably.
Where to Buy
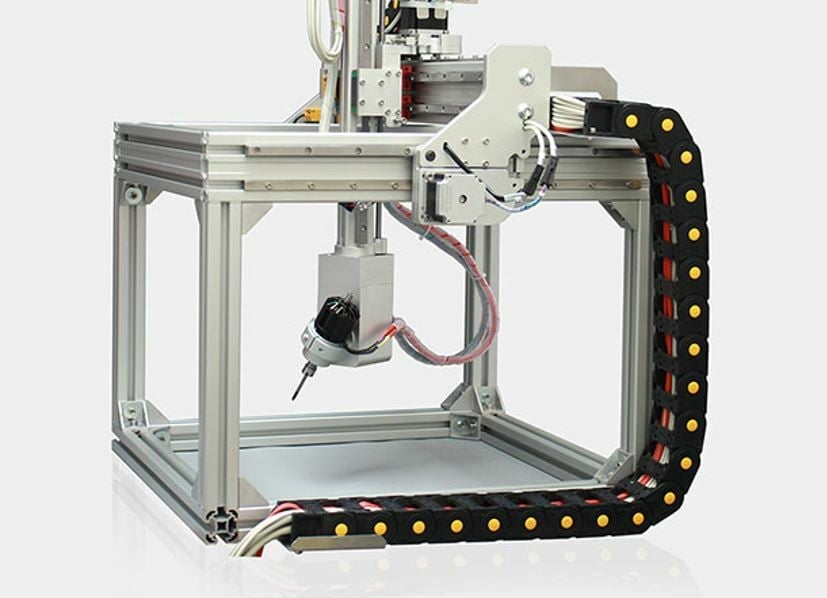

So, you’re now aware of the pros and cons and 5D printing still sounds like the kind of thing you’d like to have a bash at? Or maybe you’re just curious and want to see what’s out there?
Unfortunately, your options are a little limited, with most 5-axis printers still in the development or research stages. Yet, there are some out there available for purchase.
For a more in-depth look into the current options, plus a few up-and-coming machines, you can read our article on the latest advancements in 5-axis printing.
It’s worth bearing in mind that this is a technology somewhat in it’s infancy. When 3D printers first came onto the market, they were hard to access, expensive, and lacked support, much like 5-axis printers today.
In the years since, 3D printers have become far more accessible with even budget and kid-friendly options that produce high-quality prints. So if you’re not quite ready to jump in head-first or consider the costs too high right now, it may be worth watching and waiting on this one for a while!
License: The text of "What Is 5D Printing? – Simply Explained" by All3DP is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
