Print files can be edited using two different types of modeling software: computer-aided design (CAD) and mesh editing tools. While CAD software should always be the preferred repair method when in possession of the corresponding native file format, sometimes all you have is the converted and simplified 3D model, most commonly an STL file.
The file is no more than a shell with no filling, causing paper-thin walls and other artifacts when not properly solidified. This can lead to 3D print issues if not addressed.
CAD programs like Tinkercad, FreeCAD, or Blender can still help you out, but they’re often limited to the available information the file itself provides. Mesh editing tools like Meshmixer and MeshLab can also offer a viable alternative when it comes to editing and repairing STL files.
In this article, we’ll give you an overview of the best free CAD and mesh editing programs for your STL repair needs and include tutorials on how to get started and a few suggestions to get you fixing non-manifold edges in no time.
A manifold mesh is watertight and contains no holes or missing faces that would cause leaks into the interior of the shape’s volume. For a mesh to be manifold, every edge must have exactly two adjacent faces. A non-manifold mesh is a mesh that cannot exist in real life, and this is the reason we need to fix the meshes the majority of the time.
Once you’ve fixed your files, you can check out Craftcloud by All3DP and easily order high-quality prints from reliable manufacturers.
Tinkercad
Tinkercad is a completely free online CAD program developed by Autodesk. You can access the tool by making a free account on the Tinkercad website or logging in with an existing Autodesk account. Its main feature is its use of basic shapes and primitives as building blocks to create 3D models.
Tinkercad can be very useful for simple STL edits such as adding text, splitting a design, or combining two STLs into a single model.
The tool is easy to use, runs smoothly, and has all the basic tools you need to create a simple 3D model. However, it’s missing some key features of a proper STL editor, particularly tools for surface modeling and mesh repair.
That said, it can be a great option to help you get your bearings or to work on specific, basic editing issues if that’s all you’re after. Here’s how to do it.
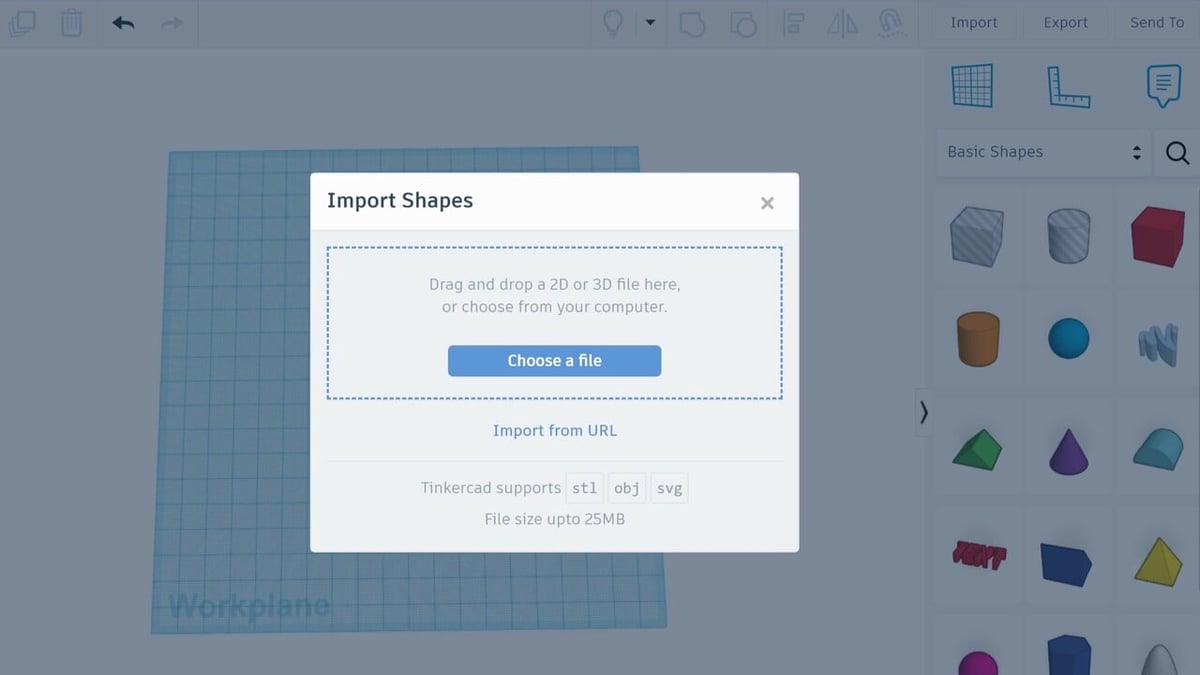
Step 1: Import an STL File
Once you have created and logged into your free Tinkercad account, you can edit your STL file. The first step is to import the file.
- Open a new design.
- Click “Import” in the upper right corner.
- Select “Choose a file”.
- Select your STL of choice, then click “Open”.
Before importing into the workspace, Tinkercad gives you a basic overview of the STL, including the part dimensions. If you need to scale your design, this is the time to do it.
- Simply enter the scaling percentage or the desired dimensions into the fields.
- Click “Import”.
It may take a minute for Tinkercad to upload the file into the workspace, depending on the complexity and file size.
Step 2: Edit STL File
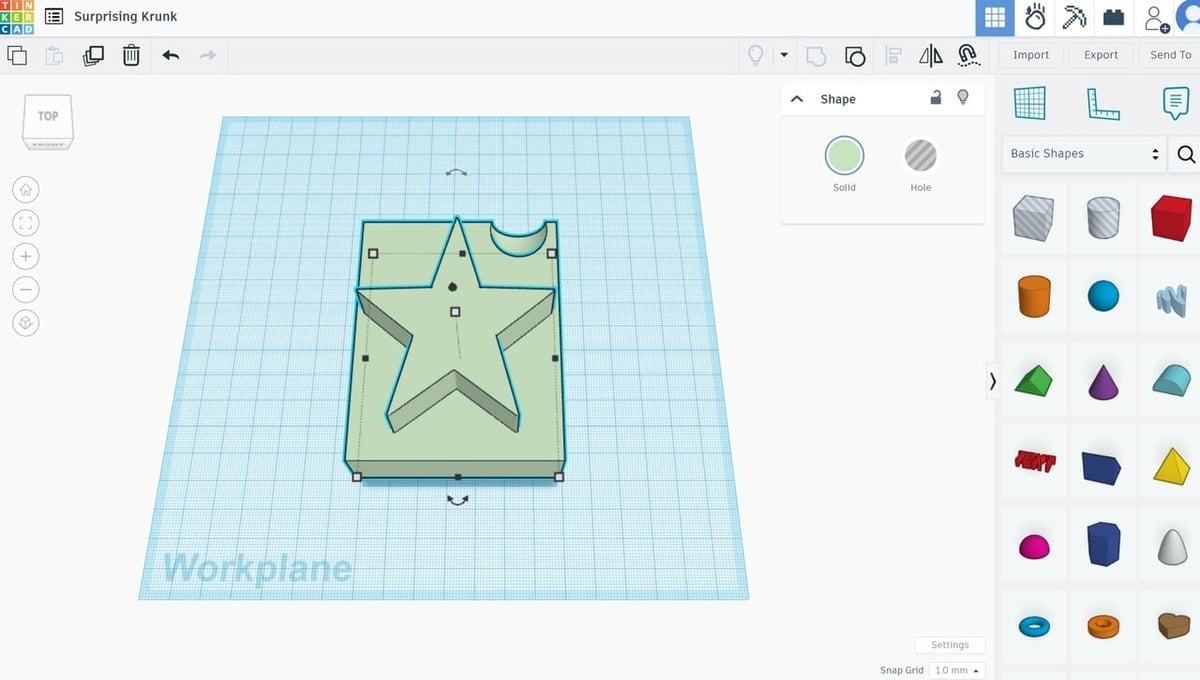
Once Tinkercad has finished importing your file, you can use any of the basic shapes, shape generators, or various other shapes provided to edit your STL. Additionally, you can import other STL files and use those to modify your design further.
- To merge two models, move them until they are combined as you want them to be, then, with both selected, click on “Ctrl + G”. To ungroup them, click on “Ctrl + Shift + G”.
- To add a hole, add a sphere from the Basic Shapes menu to the right, and locate it where you want it to add the hole in the model.
- From the top right “Shape” box, select “Hole”. Then select the other model as well (by clicking on it while pressing “Shift”), and group them (“Ctrl + G”). Your model should now have a hole.
You can also adjust size and scale using the drag points within the workspace.
Step 3: Export as STL File
Once you have edited the design to your liking, you can export it as an STL.
- Select everything you want to export.
- Click “Export” in the upper right corner.
- Follow the prompts to export the design as an STL file.
Blender
Blender is a highly diverse, feature-rich program that can be easily downloaded from the Blender project website. Blender is a great STL editor if you want to create high-poly models, offering many tools to sculpt and work out fine details. It also makes it very easy to import STL models and prepare them for modeling.
However, it has a relatively high learning curve due to its huge assortment of tools and commands. It also requires high computing power to display some models, especially if you subdivide the model into many smaller faces.
Let’s look at how you can work on your STL files.
Step 1: Open STL File
- Open Blender, click on the workspace, and delete the default cube by hovering with your mouse above it and pressing the “Del” button.
- Click on “File > Import > Stl (.stl)”, browse for the file you want to open, and import it.
Step 2: Edit STL File
- Switch from “Object” to “Edit” mode by pressing the “Tab” or selecting “Edit Mode” from the drop-down menu in the top left of the screen. You should now see all the edges your model is made of.
- Then hit ‘A’ to select all elements so the model shines orange. You can also select individual points, edges, or planes by drawing a box over them with the left mouse button.
- To convert the triangles to rectangles, use “Alt + J”.
- You can now change the number of tiles the model is made of by selecting the “Edge” tab in the top menu and then opting for “Subdivide” or “Un-Subdivide” from the drop-down menu. Alternatively, you can right-click to access the “Subdivide” tool.
This approach only increases the number of polygons by interpolating them from the pre-existing ones, meaning that your model won’t have more detail, only more faces. If you want to increase detail, i.e. surface curvature, then you need to go back into “Object Mode” and apply a “Subdivision Surface” modifier and export the resulting geometry once more as STL.
- While in Edit Mode, activate the three different selection options, “Vertices”, “Edge”, or “Face select” by pressing “1”, “2”, or “3” on your keyboard, respectively, to edit parts of the model.
- To extrude a face, select it and right-click on it. From the drop-down menu, select “Extrude Faces” and then move the face as far or as deep as you want it to go. Finally, press “Enter” or click anywhere on the Viewport. Alternatively, you can select the “Extrude Region” tool from the right-hand options.
- Search for different shapes, such as planes, cubes, or spheres, to add them to your model by going to the “Add” drop-down menu in the top of the viewport or by pressing “Shift + A” and then selecting what you need.
- In “Object Mode”, go to the Modifiers Properties in the menu to the right, and navigate “Add Modifier > Generate > Boolean”. Select whether you want an “Intersect”, “Union”, or “Difference” kind of combination with the main object, and from the “Object” selection, click on the square and select your model. Then, click “Ctrl + A” or select “Apply” from the arrow next to the operation.
Step 3: STL Repair
Apart from STL import, Blender offers a native STL repair tool.
- Activate the 3D Print Toolbox by going to “Edit > Preferences… > Add-ons > Mesh: 3D-Print Toolbox”.
- You can now access the toolbox in the right sidebar (ensure you have the sidebar enabled under “View”). You can press ‘N’ to toggle this feature and then select “3D-Print” from the tabs.
Blender’s 3D Print Toolbox allows you to address issues that might cause your STL file to print incorrectly, including:
- Overhangs that require support structures when printing with FDM and other techniques.
- Wall thickness issues that may lead to areas that cannot be printed because they are too thin.
- Manifolds that confuse 3D printers with overhanging or intersecting geometry.
You can check for all these issues by pressing “Check All” or going through them one by one. At the bottom of the toolbox, there will be a list of errors you can cycle through. To repair vertices and edges, press “Isolated”. To make your mesh manifold, press “Make Manifold”.
Step 4: Export as STL File
To export your object go to “File > Export > Stl (.stl)” and follow the prompts to save your file.
FreeCAD
FreeCAD is open-source and free-to-use CAD software that offers many different tools for 3D modeling. You can download FreeCAD for free from the FreeCAD project website. Simply select the correct version for your OS and start the installation.
While being a great software for creating exact models of technical objects, sculpting a model in FreeCAD is very difficult, as it lacks a free move-around 3D view. When it comes to editing STL files, a serious limitation is that FreeCAD struggles with intercepting structures. This may result in meshes with intercepting edges being ruined.
That said, plenty can still be done with it, so it might just be the program that suits your needs.
Step 1: Open STL File & Convert It to a Solid Model
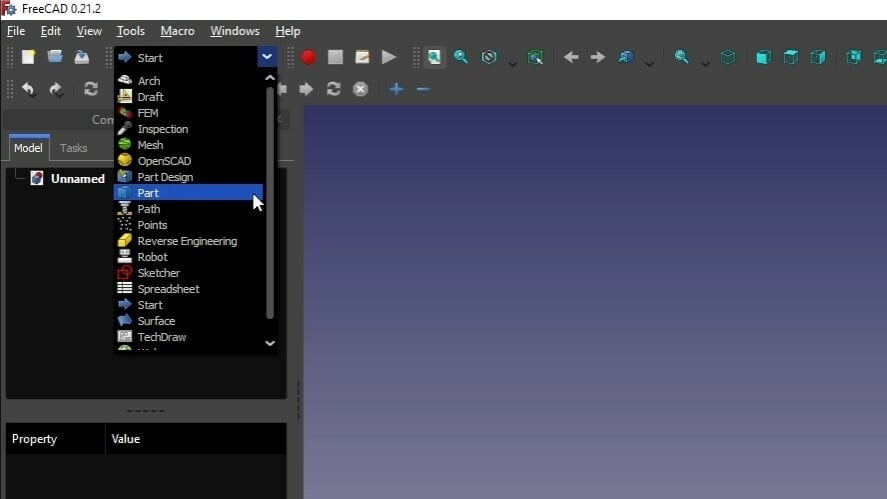
- Open FreeCAD and create a new document by clicking on “File > New”.
- Click “File > Import” and select the object you want to modify.
- Change your workbench to “Part”.
- Select the imported object in the “Model” window.
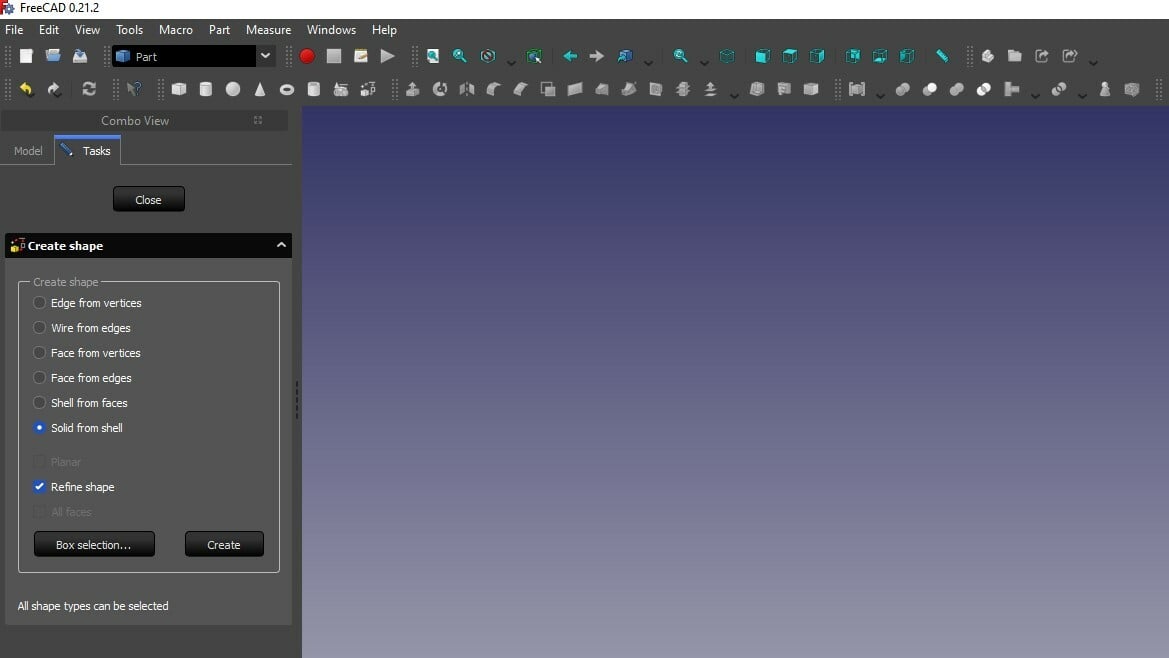
- Now click on “Part > Create shape from mesh…”. This will split up the imported object into many small triangles. You can adjust the precision of tessellation, but 0.10 is perfectly fine for most objects. If the number gets smaller, it will take longer to convert the object.
- You can now delete or hide the imported mesh. This will show you the shape of your imported object consisting of many triangles.
- Click “Shape builder” to create shapes and select “Solid from shell”. Now click on any triangle forming your imported object and then on “Create”. You will not notice anything because the shape is overlapping the solid. Click “Close” to finish.
- Next, delete or hide the old shape. You now have a solid object of your mesh file ready for editing.
Step 2: Edit STL File
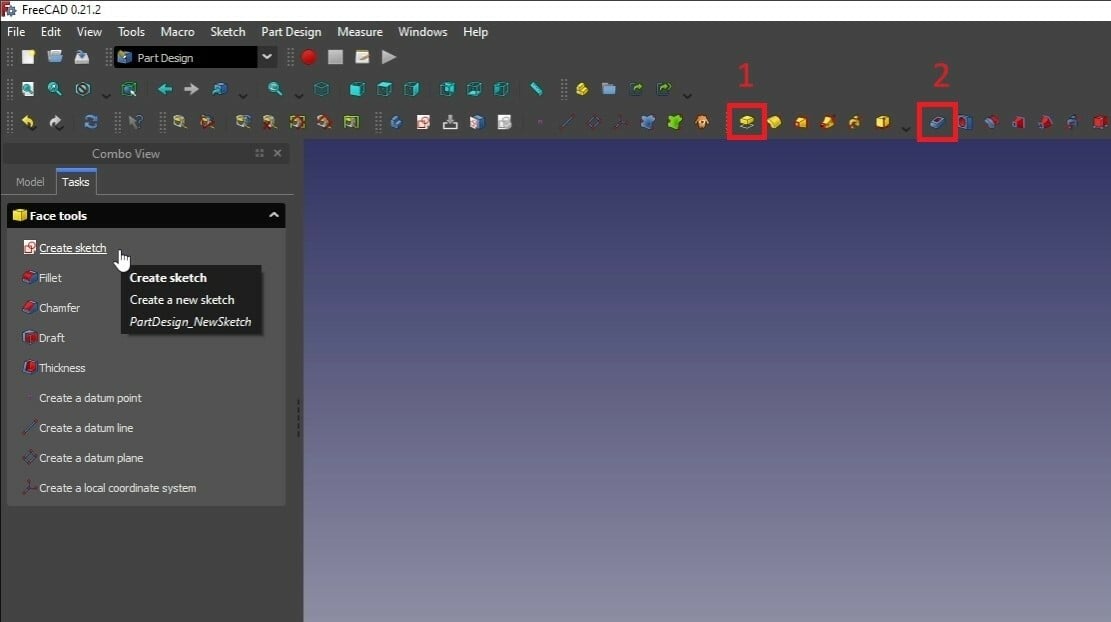
- Switch your workbench to “Part Design”.
- Click on any face you want to add or remove material so it shines green.
- Now click “Create sketch”.
- Create a shape you want to extrude or cut into using the tools for drawing a circle, rectangle, or line.
- Click on “Close” to confirm the sketch. If you want to edit the sketch, double-click it in the model tree.
- Now select a feature you want to apply. You can use the “Pad” tool (1) to extrude or the “Pocket” tool (2) to cut elements.
Step 3: STL Repair
FreeCAD also features an extensive mesh repair tool:
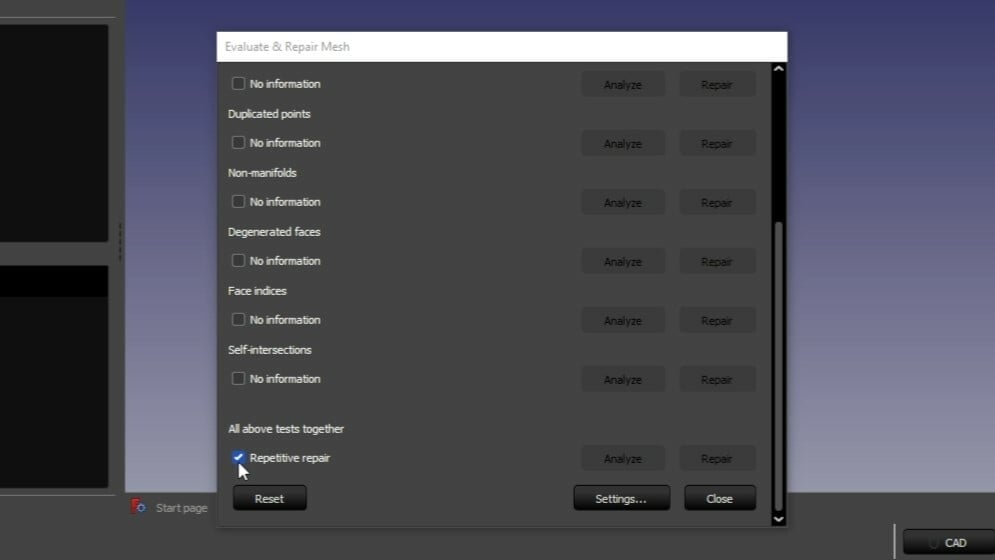
- Select “Meshes > Analyze > Evaluate & Repair Mesh”.
- From the options that appear, on “Mesh Information” select the mesh you want to repair.
- Unless you’re specifically looking to evaluate one aspect, check the box for “Repetitive repair” and then click on Analyze and then click Repair.
Step 4: Export as STL File
- Select the last feature in the model tree to export the repaired file.
- Then click on “File > Export” and select “Mesh formats”.
Meshmixer
Meshmixer is a free mesh editing program developed by Autodesk Research. It’s one of the best and most comprehensive tools for editing your STL files, being very easy to use, and having a built-in slicer. This means that you can send the edited model directly to your 3D printer for printing.
Meshmixer takes all occurring problems like paper-thin walls into account. Working with Meshmixer as an STL editor is very convenient if you just want to resize your model, change some areas, or add features to an existing design.
As of September 2021, Autodesk no longer supports Meshmixer, and the tool is no longer in development, although it’s still available for download on the Meshmixer site. Most of the tool’s popular features have been moved to Fusion, a unified CAD, CAM, and PCB software, which we’ll look at further below.
Step 1: Open STL File
- To import an STL file, simply click on “Import” and browse for your object.
- Click on “Edit > Make Solid”.
Step 2: Edit STL File
- You can now use “Select” to mark parts of your model.
- Press “Del” to remove marked tiles.
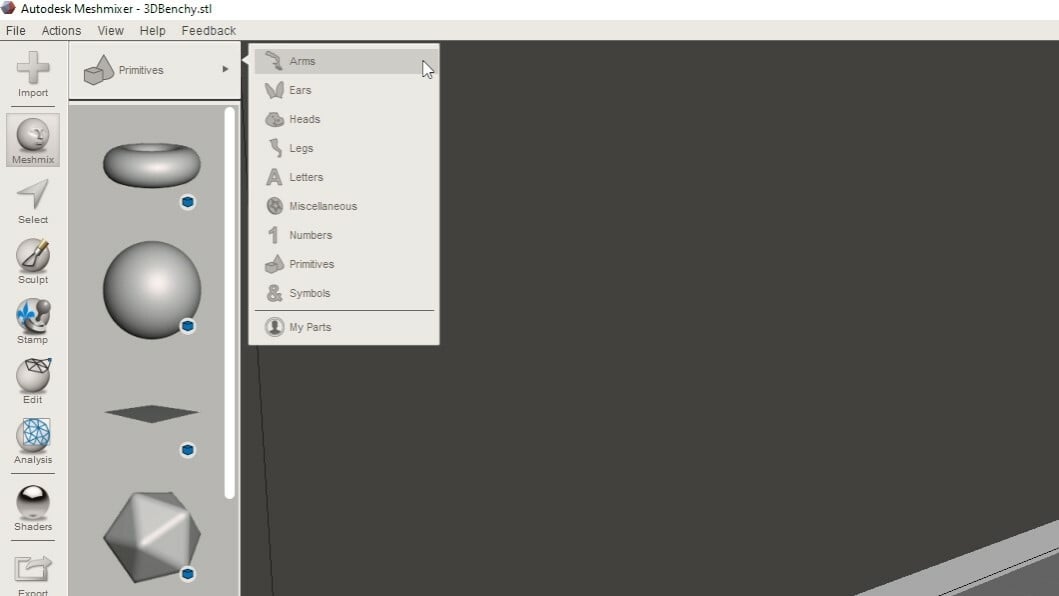
- Use “Meshmix” to open different forms. You can access more models by switching from basic forms to, for example, arms or legs. Drag and drop the object you want to insert. Use the different colored arrows to move or rotate the model. Use the little square in the middle of the arrows to scale the model.
- Click on “Sculpt” to either smooth or extrude different regions of the model.
Step 3: STL Repair & Preparation for 3D Printing
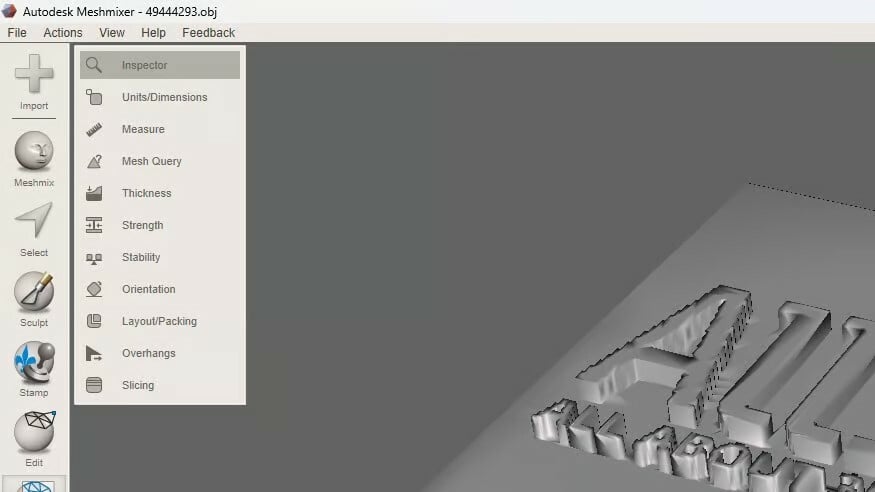
- Select “Analysis” on the sidebar. Here you find a comprehensive selection of tools that can help you prepare your STL file for 3D printing, including “Inspector” and “Overhangs”.
- Another popular method to repair STL models in Meshmixer is to go to the “Edit” option from the sidebar and select “Make Solid” to create a manifold geometry. There are a lot of settings that can severely alter the shape of the model, so make sure you understand what they do.
Step 4: Export as STL File
If you don’t want to generate supports and send it directly to the 3D printer from Meshmixer, you can export the model as an STL. To do this, go to “File > Export” and select the STL file format.
SculptGL
SculptGL is a simple 3D sculpting application that’s a great way to get started in 3D sculpting. Unlike its professional cousins, such as ZBrush or Mudbox, SculptGL includes only the basic tools necessary and gives you a sense of the sculpting workflow – all in the comfort of your web browser.
One serious flaw of SculptGL is that it can occasionally produce non-manifold vertices. However, if you’re newly curious about 3D printing, this could still be the best free editor to begin with.
Step 1: Open STL File
- Click “Scene > Clear Scene” to delete the default primitive.
- Load your STL file by clicking “File (import/export) > Add (obj, sgl, ply, stl)”.
Step 2: Edit STL File
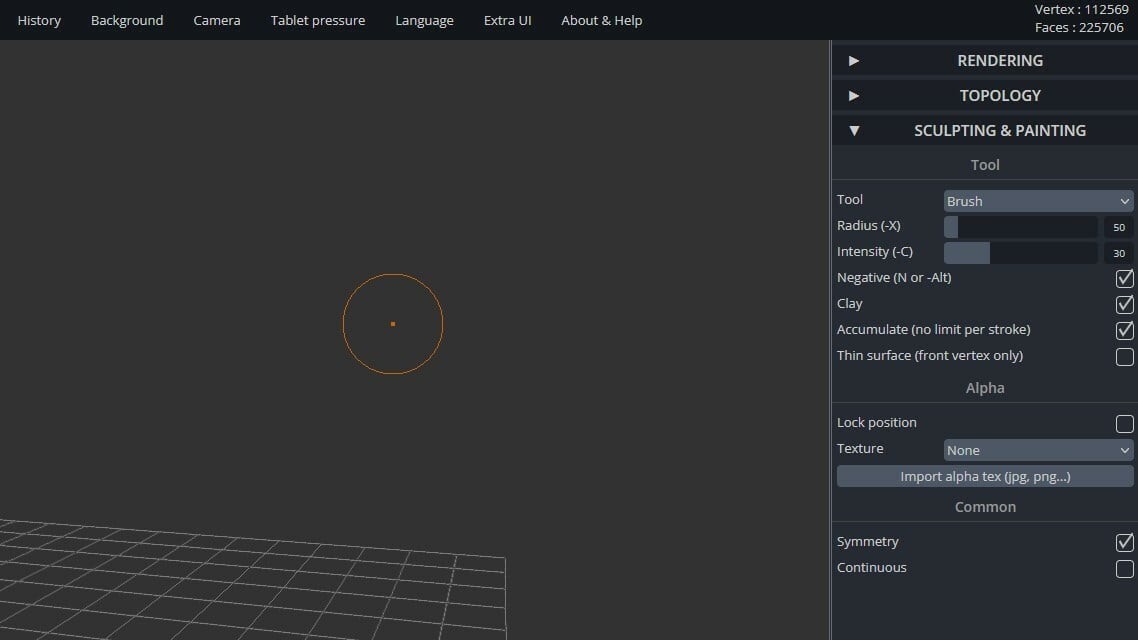
Define the big features of your mesh (arms, heads, limbs) with a large tool. Move to smaller brushes for details.
- Adjust the tool size in the “Sculpting & Painting” toolbar under “Radius”.
- Choose one of the tools to start modeling.
- You can activate the “Symmetry” button to save time. This allows you to sculpt one half of the mesh, while the other half mirrors your changes.
- If you realize that the STL file’s surface is degrading or want to add smaller details, you should increase the resolution. To do this, there are two options. First, you can subdivide the mesh by selecting “Topology > Multiresolution > Subdivide”. Or you can remesh the mesh. To do this, select a resolution at “Topology > Voxel Remeshing > Resolution”, then click “Remesh”.
Step 3: Export as STL File
This step is as simple as it gets: Click “File (import/export) > Save stl”.
MeshLab
MeshLab is a free open-source program that allows you to view, merge, transform, or repair STL, PLY, OFF, OBJ, 3DS, and many other file types as well as point clouds.
MeshLab doesn’t offer the option to create new objects, but it is still a great choice for combining or repairing a mesh. You can easily combine the mesh of a 3D scan or even create new models by merging them.
You can download MeshLab for free from the project website.
Step 1: Open STL File
To open a supported mesh file, go to “File > Import Mesh” and browse for your model.
Step 2: Edit STL File
MeshLab doesn’t have the tools to create new vertices or objects. However, it is a great tool for combining two meshes of a 3D scan. You can also remove parts of the mesh and repair holes in the model.
Merging Two Meshes
- First, load both models.
- Click on “Show Layers”. Select the models in the workspace.
- To transform, rotate, or scale an object, first select it in the “Layer” menu and then click on “Manipulator Tools”.
- You can now press ‘T’ to select the “Transform” option. Click on ‘R’ to rotate the model and ‘S’ to start scaling.
- The direction you are looking at the model determines the coordinate system you are working in. Simply drag and drop the arrows to move or scale the model in one direction. Turn the circle around the object to rotate it. When you want to rotate your view, press “Escape”, and when you have the desired view on the object, press “Escape” again to continue transforming. Press “Enter” to confirm the placement.
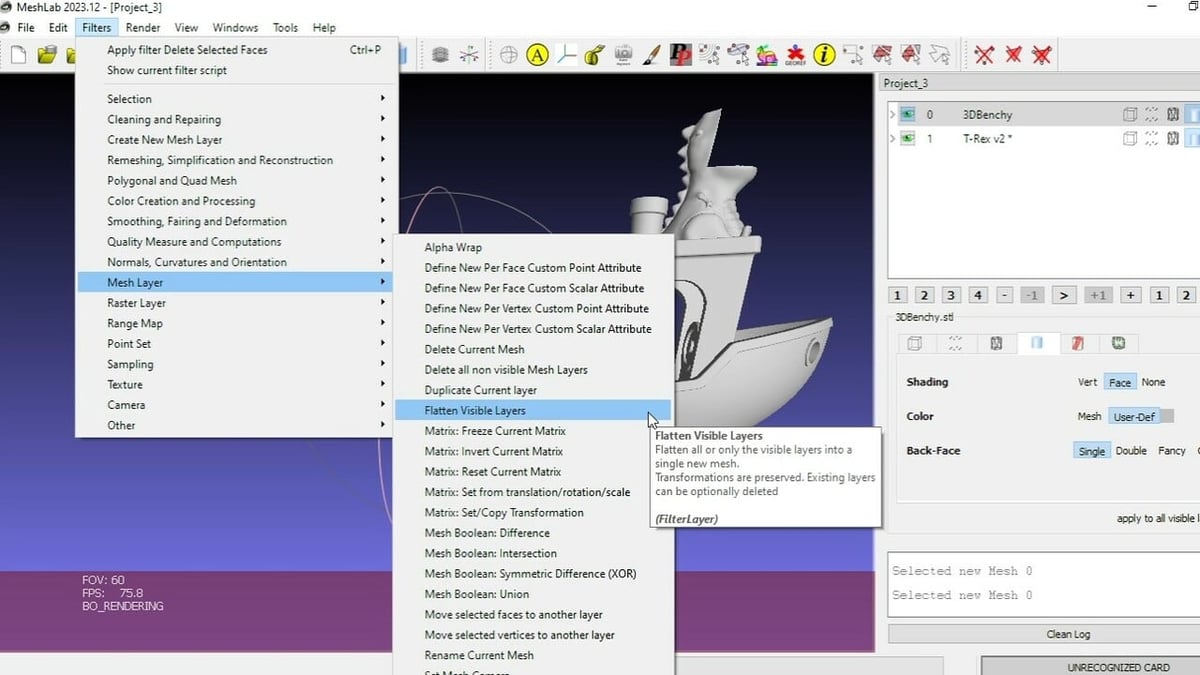
- When you have put all the parts in place, go to “Filters > Mesh Layer > Flatten Visible Layers”. Check the first three boxes and click on “Apply”.
Deleting a Section
- To delete a part of the mesh, click on “Select Face” in a rectangular region.
- Then click “Delete the Current Selected Face and Vertices”.
Repairing Your Object or Searching for Holes
- Click on “Fill Hole”. Your model must be manifold for this option.
- A window will pop up and show you all the holes in the model. You can now select the holes you want to fill. They will shine green when selected. Click on “Fill” and then on “Accept” to finish.
Step 3: STL Repair
- To check if your STL file is watertight select “Filters > Quality Measures and Computations > Compute Geometric Measures”. You should see a volume for your file or an error report in the dialog on the right side.
- In case your STL file is not watertight, select “Filters > Cleaning and Repairing > Merge Close Vertices”, then click “Apply”. Next, select “Filters > Cleaning and Repairing > Remove Duplicate Faces”, and click “Apply”. Finally, select “Filters > Cleaning and Repairing > Remove Duplicated Vertices”.
- Recheck your STL file.
Step 4: Export as STL File
To export the model, go to “File > Export Mesh”.
Fusion 360
Fusion (until recently known as Fusion 360) is a cloud-based 3D CAD/CAM software developed by Autodesk. It can be used for free on its personal use license, which has certain limitations but fortunately provides access to powerful mesh editing and creation tools. These tools support both parametric and direct modeling modes where you can insert, repair, and modify mesh bodies to prepare them for manufacturing.
It’s good and practical software to work with. While the learning curve can be steeper than simpler programs such as Tinkercad or Meshmixer, there’s plenty of information about how to use it, and once you get used to the user interface and tools, it naturally becomes a powerhouse for 3D modeling.
Step 1: Open STL File
- On the Design workspace, select the Mesh Tab.
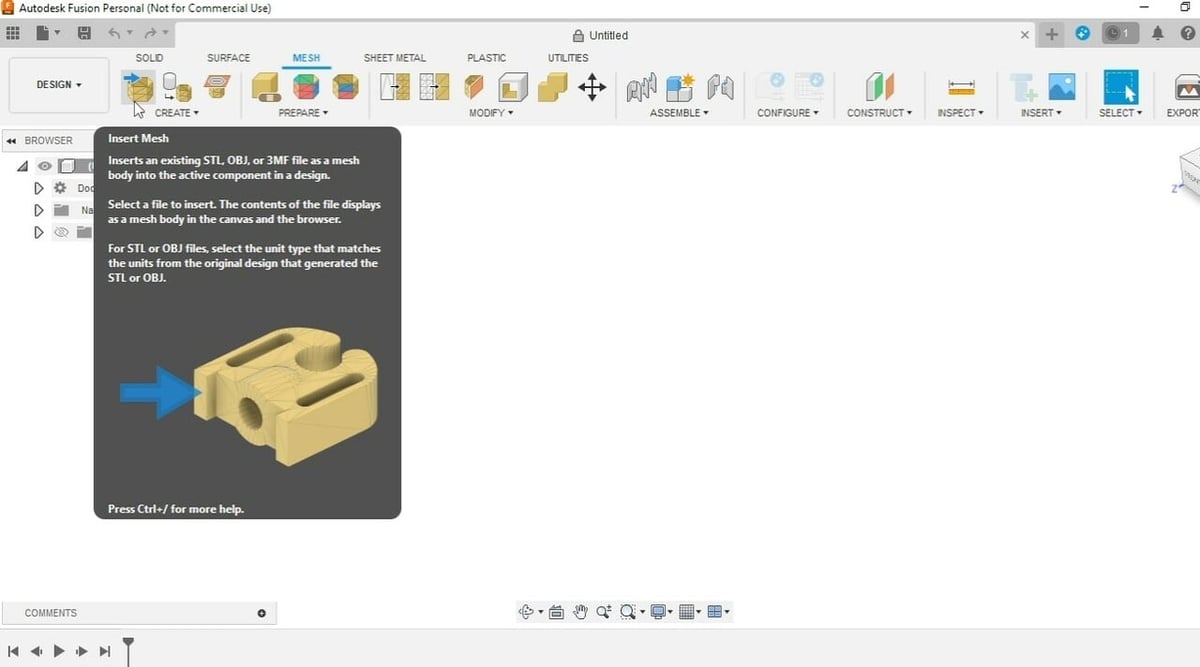
- In the Mesh tab, from the “Create” group, select “Insert Mesh”.
- You can select a mesh from your cloud files or from your computer. Accepted file types include STL, OBJ, and 3MF.
- This will load the mesh and a window will pop up on the right. There you can flip the direction and click “Okay” to finish the process, to make the mesh normals face out.
Step2: Edit STL File
- Many editing commands are available from the “Modify” group, such as Combine, Smooth, Plane Cut, and Scale.
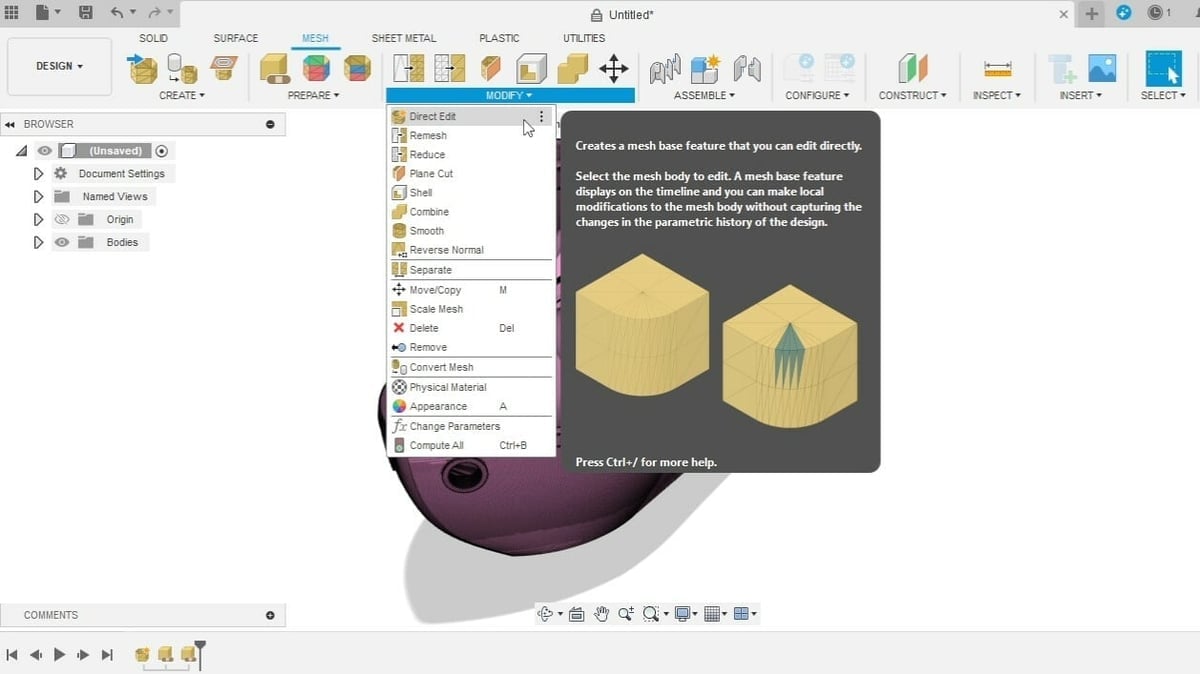
- You may also use the “Direct Edit” tool, with which you can make direct modifications to the mesh body without capturing the changes in the parametric history of the design. With that, all the modifications will be kept in a single instance on the history line.
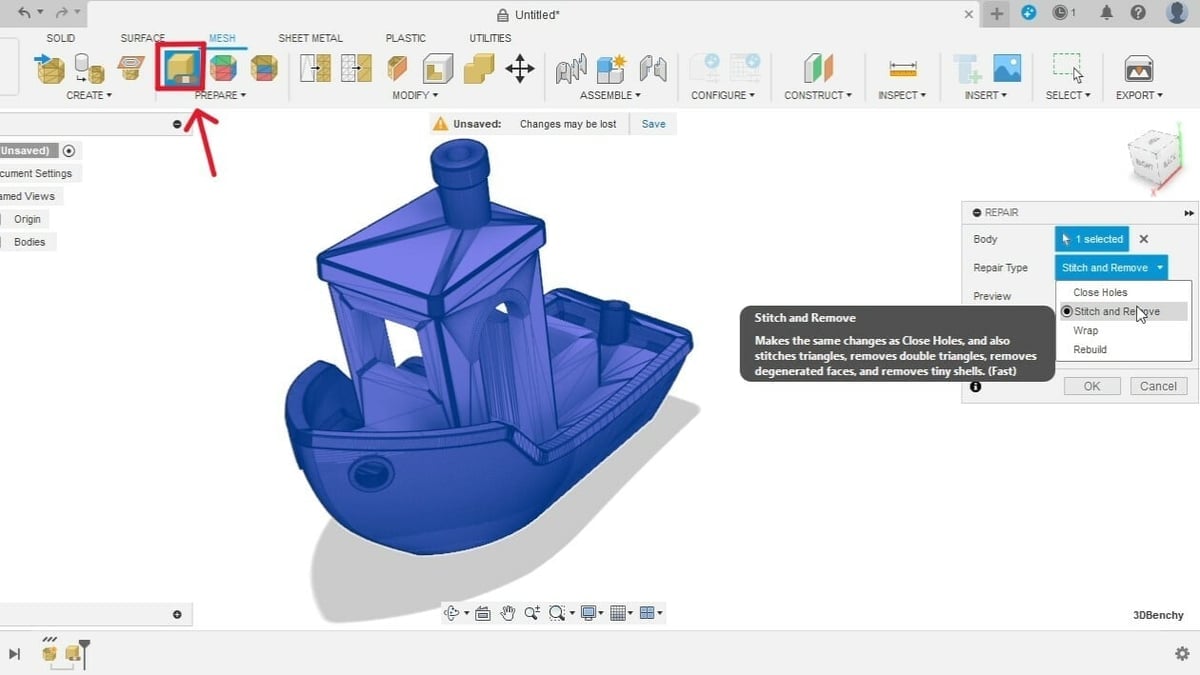
Step 3: STL Repair
- From the “Prepare” group, select the Repair command.
- This will open a pop-up window on the right, where you can select the bodies to modify.
- The Repair Type options include Close Holes, Stich and Remove, Wrap, and Rebuild.
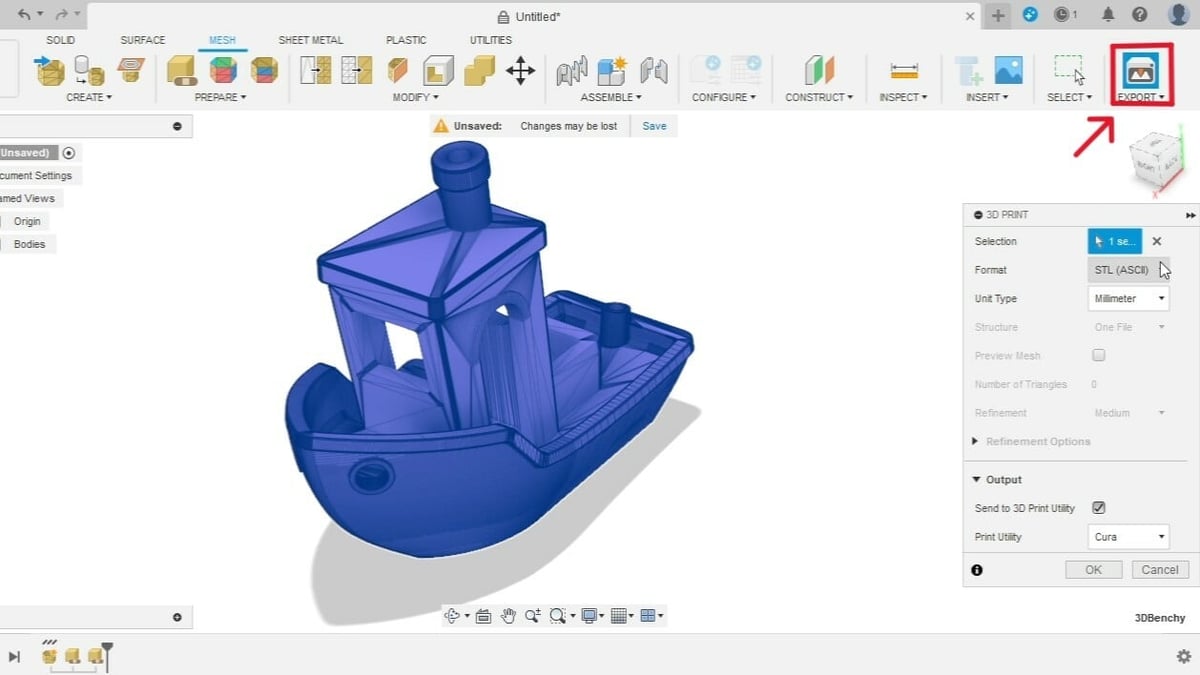
Step 4: Export as STL File
- In the Export group, select the 3D print command.
- On the window that pops up to the right, select the mesh bodies to export, the desired file format, and the unit type.
- You have the option to output the mesh directly to the slicer by checking the box for “Send to 3D Print Utility”.
- Otherwise, leave it unchecked and you can download the mesh.
License: The text of "Free STL Editors: How to Edit & Repair STL Files" by All3DP is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.