3D printing is becoming an increasingly popular technology among small businesses, but also independent creators. Thanks to the introduction of affordable 3D printers, anyone can now start creating from the comfort of their home. Some of us take the word “desktop” literally, having the printer working next to the computer.
We know all about the convenience of 3D printing, largely due to its capabilities to help print any desired shape using a wide range of materials. However, not much is known about the technology’s medical and environmental impact.
New research by the German environmental association Umweltbundesamt has now taken a closer look at additive manufacturing in the context of environmental and personal health.
Environmental and health impacts
On the one hand, there are high hopes for 3D printers to help solve environmental challenges such as the printing of coral reefs to help restore those dying in the oceans. At the same time, a systematic assessment of 3D printing processes found that it affected greenhouse gas emissions due to its high energy demand.
The technology also contributes to indoor air pollution due to particulate matter and nanoparticles from materials. This concerns particularly power-based and extrusion methods as well as stereolithography, which all contribute to the release of particulate matter that is 10x higher than the values suggested by the US Environmental Protection Agency.
Additionally, this presents a significant health burden on employees who come in contact or inhale nanoparticles. Right now such exposures are still largely restricted to industrial workplaces.
Furthermore, most plastic materials employed in additive manufacturing continue to be petroleum-based. It is well established that the manufacture of petroleum contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
The environmental impact of 3D printers thus partly depends on the materials used with plastics and metals generally having a greater negative impact than renewables.
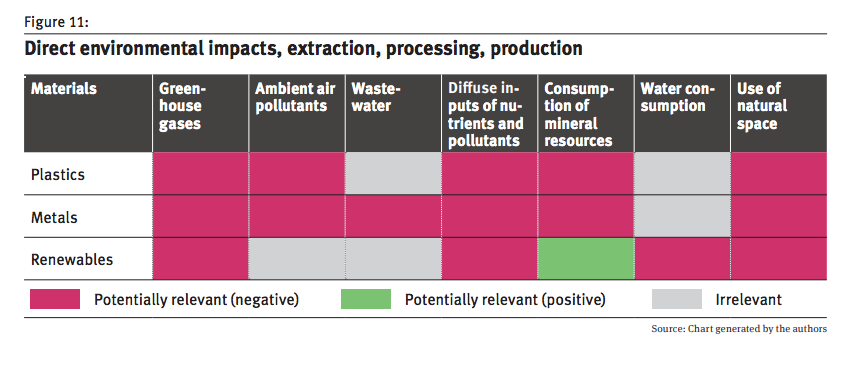
Environmental burden of 3D printing. (Image: Umweltbundesamt)
Industrial application
There are many reasons why industrial manufacturers increasingly use 3D printers. For example, car manufacturers utilize additive manufacturing to speed up the creation of prototypes.
Prototype printing can significantly reduce the use of materials and requires fewer resources and energy than conventional methods. This offers a potential benefit in terms of environmental impact.
Similarly, the report notes that the repair of spare parts can have a lesser impact on greenhouse gases than other methods. Tool production and recycling may also help reduce the environmental burden compared to traditional manufacturing methods. The same is not true for personal desktop 3D printers.
Bio-printing, in particular, has some of the potentially greatest benefits in terms of environmental impact. By being able to print organic animal tissue from cells, we could potentially revolutionize the food and leather industries. Artificial meat requires 45% less energy and causes 96% fewer greenhouse gas emissions. It also uses 99% less land and 96% fewer water compared to conventional meat production.

Some of the positive impacts of 3D printing. (Image: Umweltbundesamt)
Other impacts
Lastly, the report assesses potential impacts that are harder to assess given that additive manufacturing is still not heavily used. This includes the impact on trading by an increasing prosumer movement. Indeed, if more people own desktop 3D printers they could print more of the products they may need regularly. This could result in a reduction in trading opportunities.
At the same time, allowing people to innovate more easily helps to fuel a bio-industry that focuses on the development of more sustainable products.
The report concludes that 3D printing offers both opportunities to enhance the development of environmentally beneficial industries whilst presenting a burden on select environmental areas.
Further research is necessary to elucidate the full and long-term effects of 3D printing on the environment and personal health.
You can download the free study here.
Source: Umweltbundesamt
License: The text of "New German Study Concludes 3D Printing Health Challenges" by All3DP is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.