What Is It?
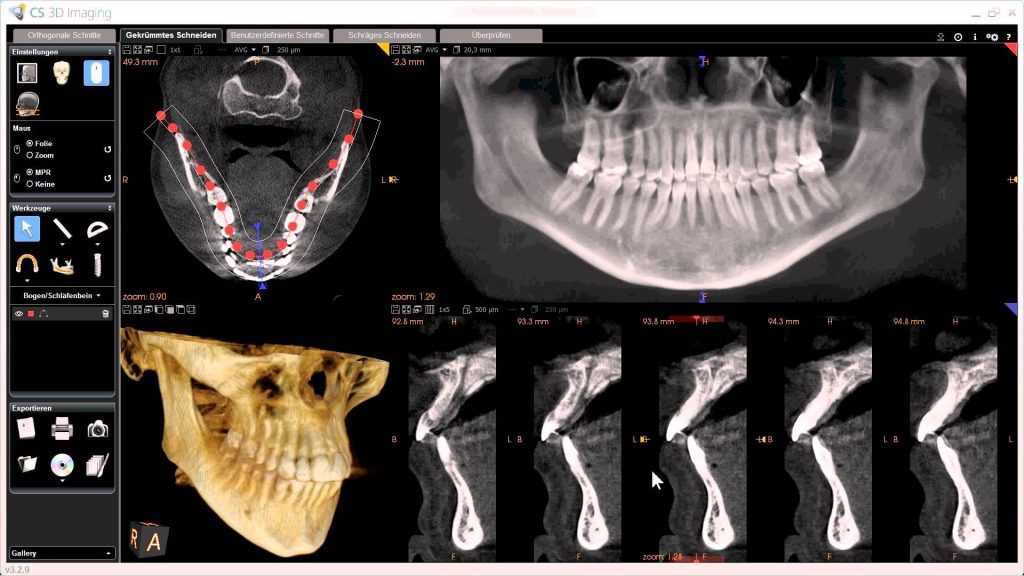
3D dental imaging is slowly becoming the new standard of care in dental practices. 3D dental scanning allows dentists to digitally reconstruct your teeth and skull in 3D. Dental practitioners can interact with this 3D model and visualize aspects of the model that would otherwise be difficult or impossible to access. This new perspective allows clinicians to more effectively diagnose an issue or provide a more effective means of treatment.
3D dental scanning is most commonly utilized for cosmetic and restoration purposes, such as reconstructive therapy or oral surgery. 3D imaging allows for planning and customizing services for procedures such as bone grafts, implants, and root canals. 3D scanning is also often used to create 3D images for orthodontic treatment.
Advantages
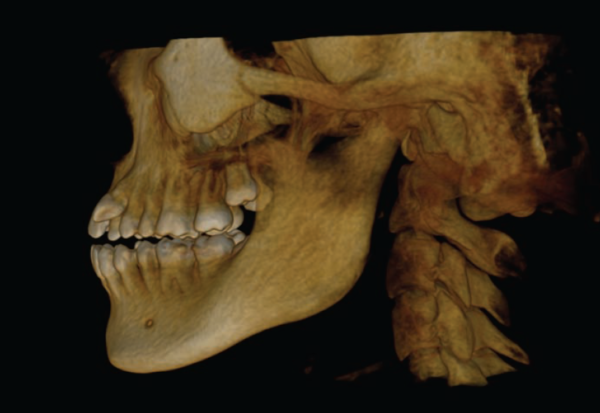
Because of the way 3D scanners work, there are multiple advantages over traditional dental imaging methods:
- Reduced radiation: Dental scanners reduce the amount of radiation the patient is exposed to, as they require little time to scan and focus on particular regions.
- Three dimensions: Unlike conventional techniques, dental scanners provide 3D models, which offer much more information over 2D images.
- Exceptional accuracy: 3D images provide far greater detail compared to using molds. Dentists are able to see pathologies, infections, nerves, musculature, and more.
- Efficiency: Scanning using 3D dental scanners is much less time consuming than traditional molding or imaging methods.
- Synergistic technologies: Data from multiple 3D scanning technologies can be combined to produce increasingly accurate models.
- Non-invasive: There’s no need to bite down on a mold or piece of plastic as you can scan the entire head or the specific region of the mouth while the patient patiently waits.
How Do Dentists Use Dental Scanners?
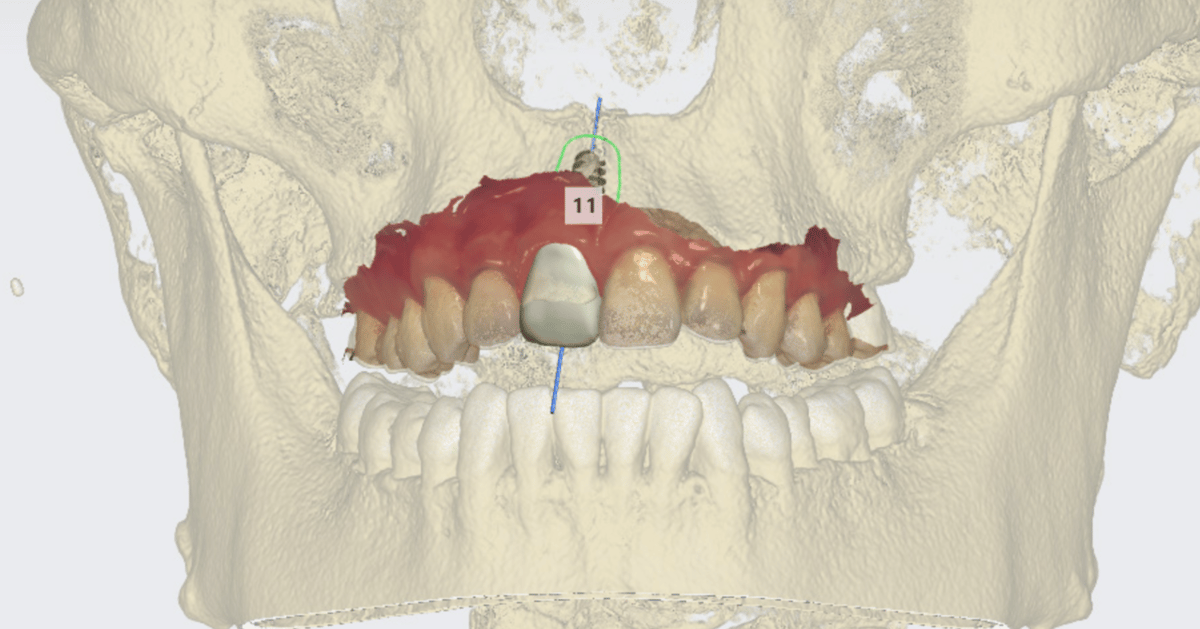
By digitizing the workflow, dental clinicians can more effectively treat and streamline procedures for patients.
For example, a patient that requires an implant can be scanned by a 3D dental scanner (sometimes two different types of scanners) to assess the situation and generate a CAD model of the patient’s mouth. A digital plan for the implant is also generated in CAD software to meet the requirements.
Such a model can be sent to design labs for fast fabrication, to be used in surgery the very next day. Moreover, with access to the digital plan, surgery can be performed more efficiently, as the surgeon is able to familiarize himself with the patient’s operative area.
This digital workflow can be applied to multiple dental processes, like creating low-cost functional dentures based on digital impressions or replacing multiple porcelain veneers with all-ceramic veneers.
There are multiple types of 3D dental scanners employed by clinicians in practice. Let’s look at the three main types of scanners and how they work.
Dental Scanning Technology #1: Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)
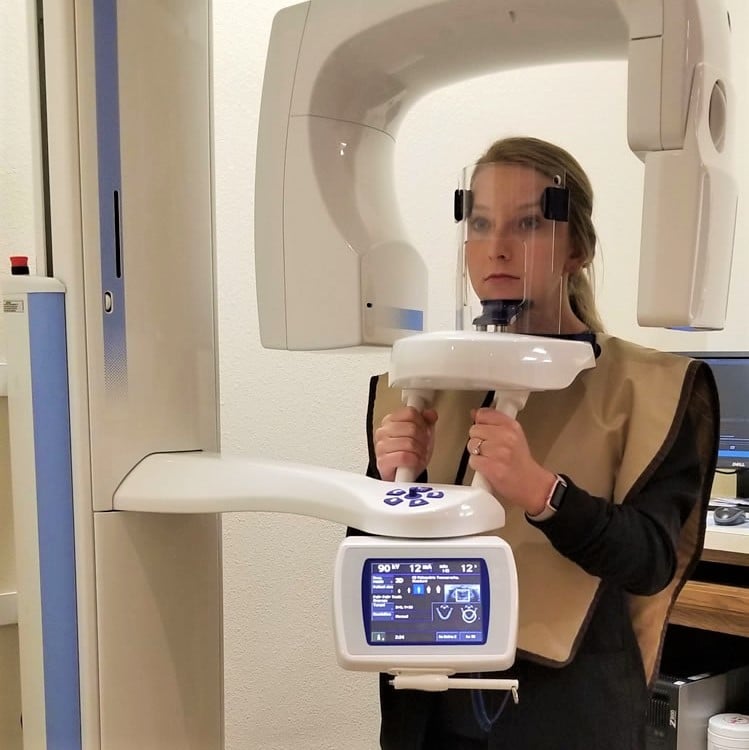
Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) machines take scans of the mouth and face using a series of small beams of X-ray radiation on a 360-degree rotating axis. The imaging systems typically rotate once around your head while you stand or sit in a chair. The process is extremely quick, simple and non-invasive.
Once taken, the series of images are stitched together into a 3D model. Today, CBCT is also being used in radiotherapy and mammography because it’s more effective and safer than medical CT scans.
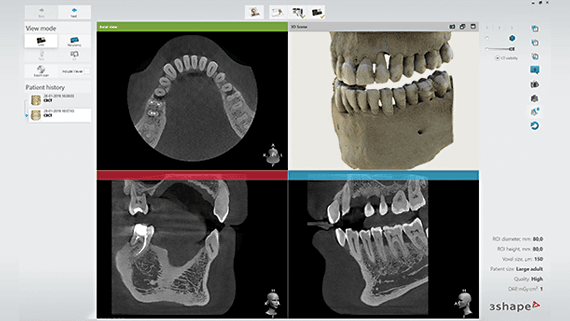
Example CBCT Scanner: 3Shape X1
The 3Shape X1 CBCT scanner is the industry’s first scanner without head fixation for a more comfortable patient experience. 3Shape X1 uses motion correction to provide more accurate 3D reconstruction and a dynamic field of view to provide even sharper images.
Dental Scanning Technology #2: Intraoral Scanner (IOS)
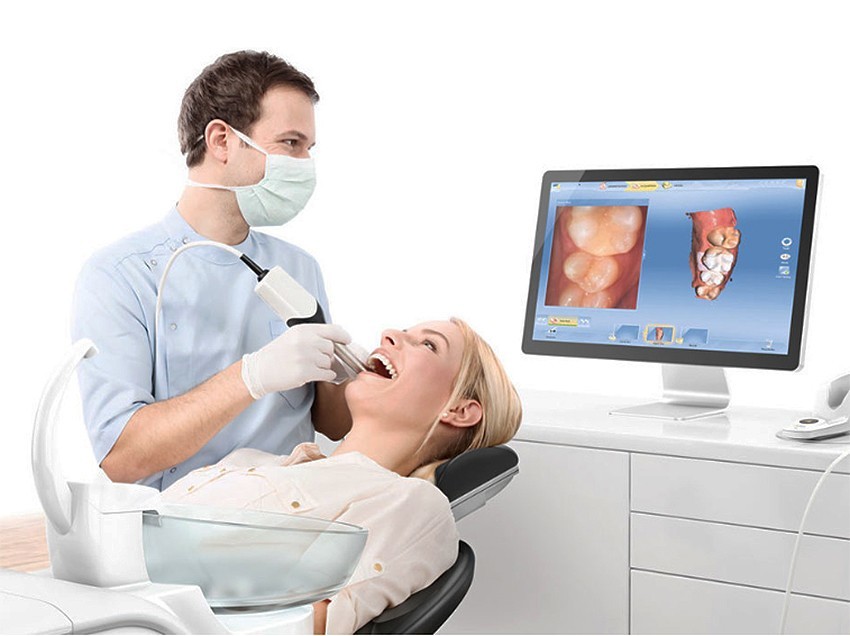
Intraoral scanners (IOSs) are handheld devices used to capture direct optical impressions in dentistry. They are essentially cameras that project light onto an object such as a dental arch, creating a coordinate map used to generate a 3D surface model.
Mostly commonly, IOSs exist in the form of a “wand”, which the operator can directly insert into a patients mouth. They’re typically designed to be easy to use, with light, ergonomic grips and detachable tips of varying sizes.
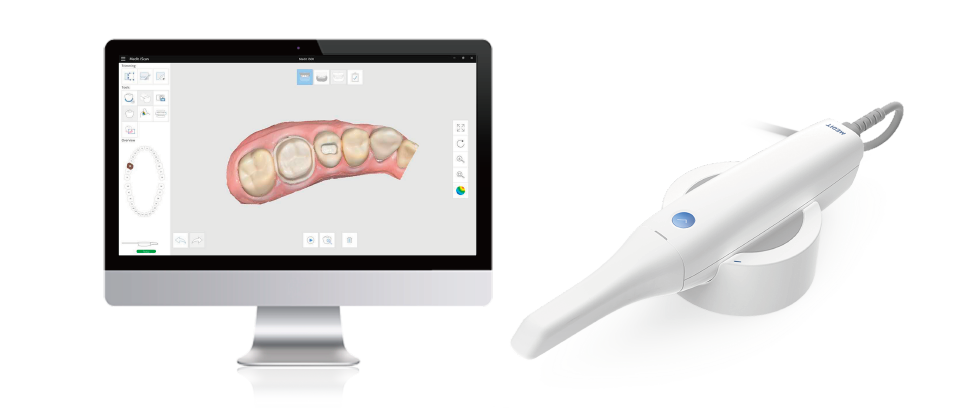
Example Intraoral Scanner: Medit i500
The Medit i500 provides easy entry into digital dentistry. Their system is open, allowing for easy movement between CAD and CAM software as well as optimized collaboration. The scanner also uses two high-speed cameras to provide faster scanning.
Lastly, unlike some IOSs, the Medit i500 is powderless, allowing for a more seamless and efficient scanning process and greater patient comfort.
Dental Scanning Technology #3: Lab Scanners
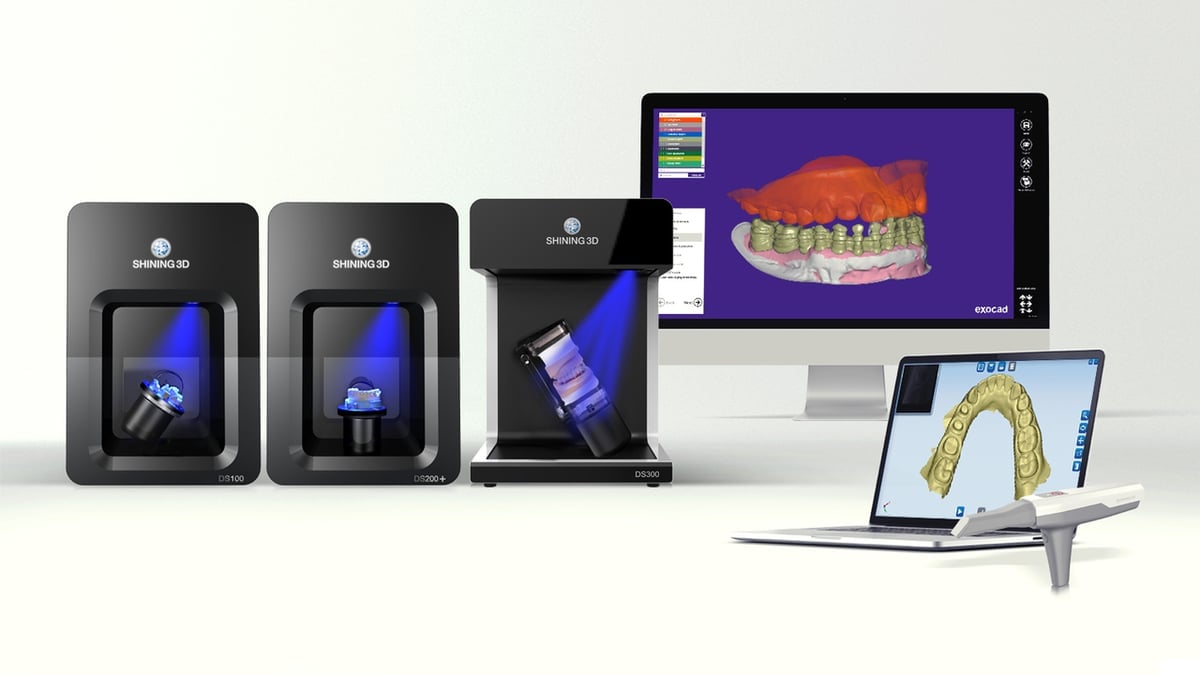

Dental lab scanners work like traditional 3D scanners and are therefore more typically used to scan items outside the mouth.
Using cameras, light, and rotating platforms, these devices are used to scan a wide variety of dental designs, like restorations, orthodontics, implant cases, and articulators. Digitizing these objects allows clinicians to easily make modifications and streamline production.
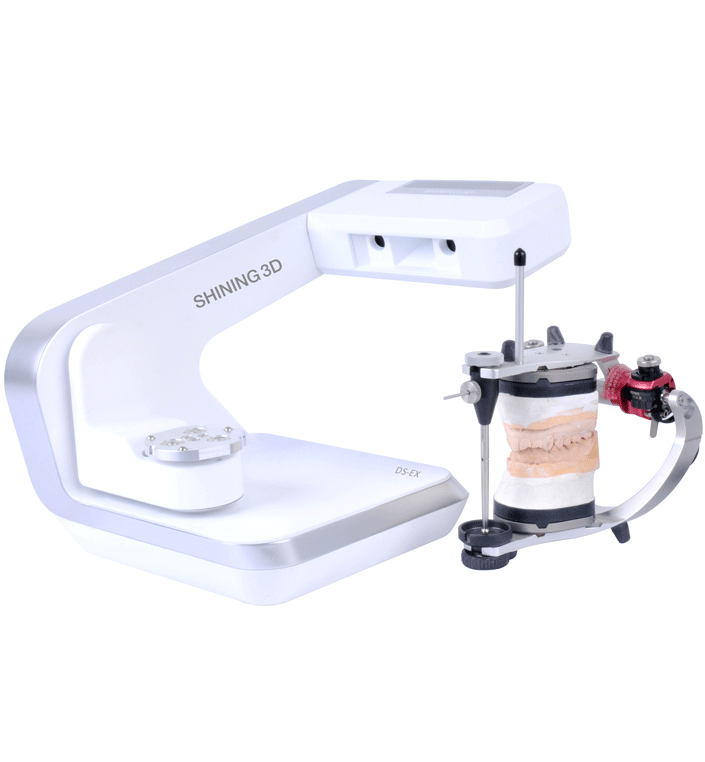

Example Lab Scanner: Shining 3D Autoscan-DS-EX
The Shining 3D lab scanner is small and lightweight, making it extremely useful for labs with restricted space. It supports scanning a wide variety of articulators with multiple scanning functions and a specific “Clinic” mode to support chair-side restoration solutions.
Similar to the Medit i500, this scanner also uses an open data format to export STL files into any CAD/CAM software.
Feature image source: 3shape.com
License: The text of "Dental 3D Scanning – Next Level Imaging in Dentistry" by All3DP is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.