What Exactly is It?
Using the Internet to learn something new can be useful, but sometimes it’s hard to find information that’s completely accurate. You might, for example, stumble across the term “3D laser printer” and begin to wonder how lasers could be used to build parts.
The tricky thing here is that “3D laser printer” isn’t a proper term. If you see it, it’s probably being used to refer to one of two things: an SLA or an SLS 3D printer. That’s because both employ lasers to create 3D objects, although they go about it in very different ways. Let’s take a closer look at both.
Stereolithography (SLA)
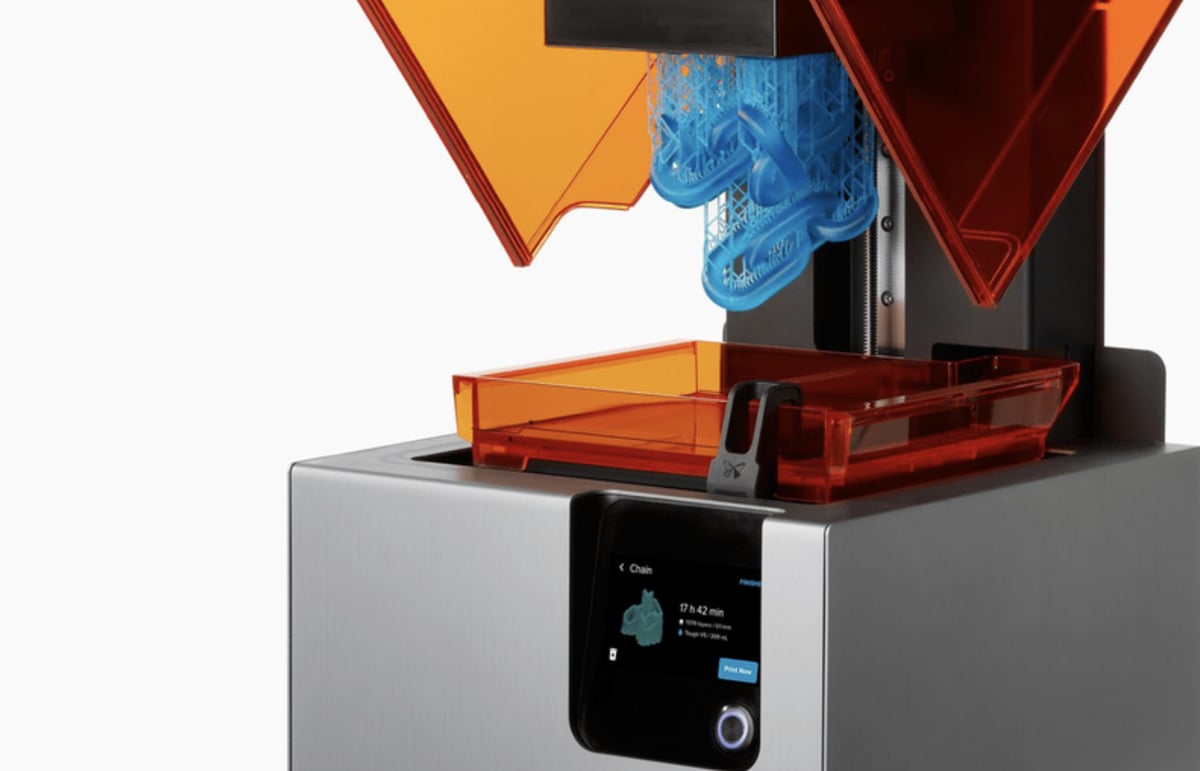

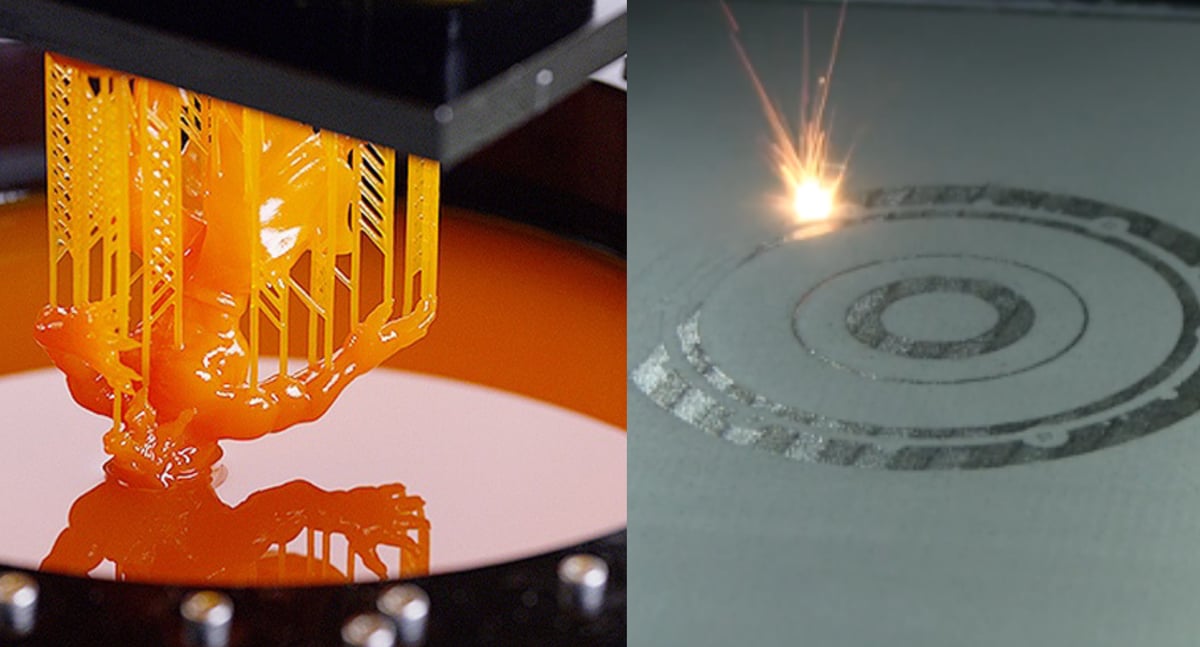
Stereolithography, or SLA, was the first 3D printing technology. It uses the UV light from a laser to selectively cure a photosensitive resin, thus turning into a solid. Apart from the laser, an SLA 3D printer consists of a resin tank and a build platform, which is supported by an elevator.
The build process using an SLA 3D printer begins with the user filling the resin tank. After that’s done, the build platform dives inside the resin tank, leaving only one layer in height between it and the floor of the resin tank. The laser is positioned beneath the resin tank and shines up through its floor, which is transparent. The layer then “draws” the first layer of the part, curing the resin to a specified shape. After each layer is cured, the build platform moves up one layer in height and the process continues until the part is finished.
If you’d like to learn more about SLA, feel free to click here.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)

Selective laser sintering (SLS) also utilizes a laser, but the process is quite different from that of SLA. The biggest difference is the material the technology uses. Instead of a photosensitive resin, SLS uses a polymer in the form of a fine powder, and the laser fuses the particles together.
In addition to the laser, an SLS 3D printer consists of a powder bin and a build platform capable of moving up and down.
The print process begins with filling up the powder bin with a layer’s worth of powder. Onto that coating, the laser “draws” the first layer of the print, sintering the powder into a single solid. Following each layer, a new coating of powder is spread atop the old, and the process continues until the object is complete.
If you’d like to learn more about SLS, click here.
Misnomer
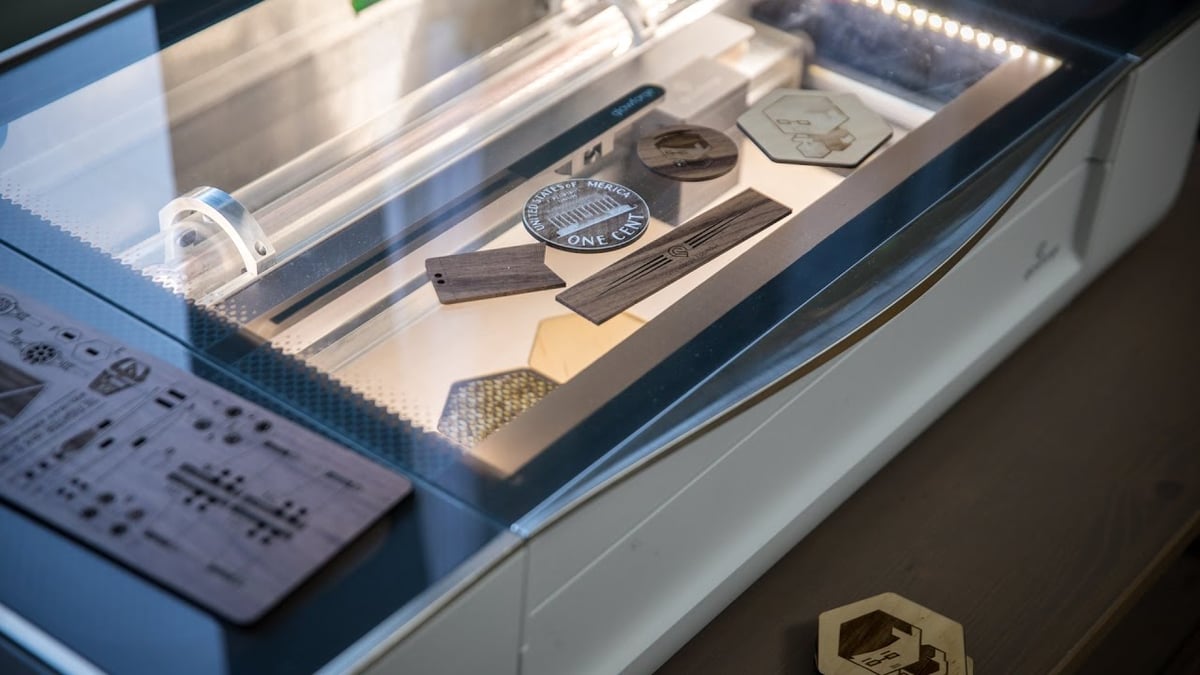

Outside of the above technologies, there is one other thing “laser 3D printer” could refer to: the Glowforge. It claims to be a “laser 3D printer” but is actually a laser cutter.
The Glowforge is user-friendly and works on a wide selection of materials, from cardboard to aluminum! A specific feature that caught our eye is the ability to personalize your laptop by engraving custom design on the backplate of your laptop. Apart from that, you can also cut wood, leather, and even chocolate!