Swiss Researchers Begin Construction of the DFAB HOUSE
The DFAB HOUSE is the world’s first building made from predominantly digital processes by a collaboration of professionals in Zurich.
Over the past few years, the world has seen huge leaps in digital fabrication processes for building applications. Which is why eight professors at ETH Zurich decided to team up to push these new processes to the limit.
The new pilot project in Switzerland has a range of professionals and disciplines from ETH Zurich working together to create a three-storey building. These include robotics specialists, material scientists, architects, structural engineers, and sustainability experts.
The project is part of the National Centre of Competence in Research (NCCR) Digital Fabrication. The DFAB HOUSE uses new digital building technologies from the ETH laboratory. As a result, the entire project — from design, and plan to final build — relies on these emerging technologies. Moreover, it reduces or bypasses the need for traditional methods.
The ETH professors also want to examine how construction can become more environmentally friendly. The final aim of this project is to explore sustainable and efficient building processes.
3D Printing and Building the DFAB HOUSE
Construction began on the DFAB HOUSE at the modular research building for Empa and Eawag, called NEST. The building is on campus at Dübendorf and here, researchers can test technologies under real conditions.
For the DFAB HOUSE construction, researchers are using four research methods. Once they have completed initial testing phases, the methods will be ready for further tests in real world applications.
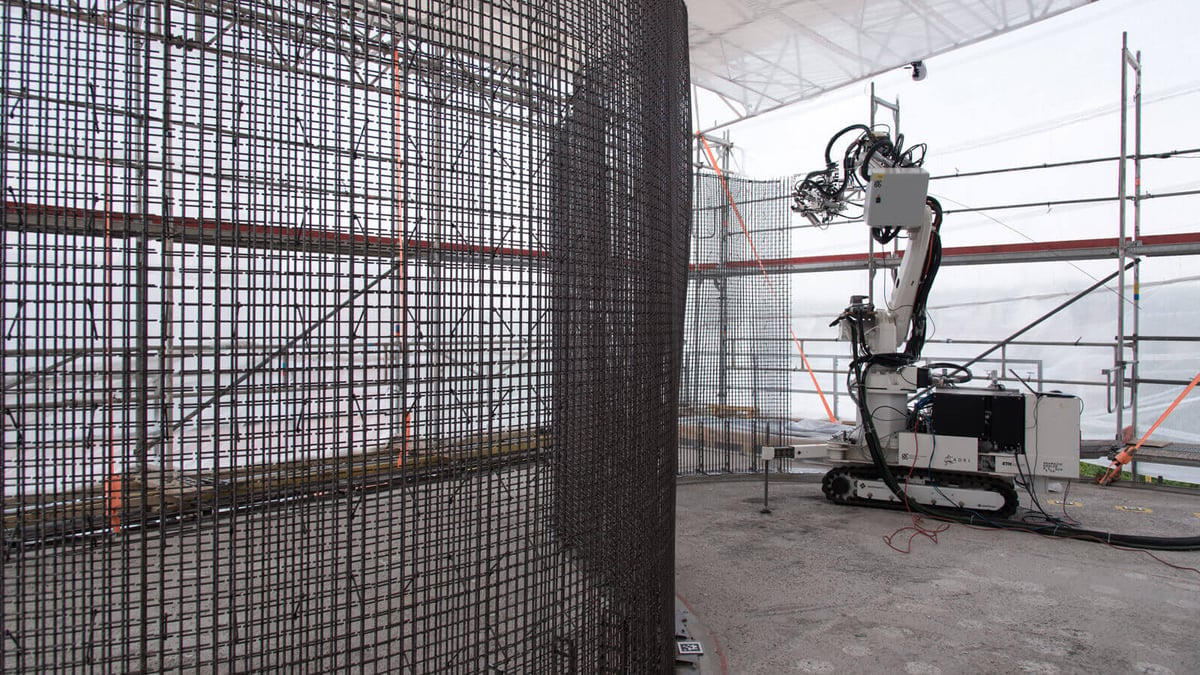
Firstly, the professors are using Mesh Mould technology, which “is a waste-free robotic fabrication process for fully loadbearing, non-standard concrete constructions.” This will provide the structure with a double-curved load-bearing concrete wall.
The researchers are then incorporating a “Smart Slab” which is a “statistically optimised” ceiling slab. For this, a large-format 3D sand printer develops the framework.
Smart Dynamic Casting technology is automated robotic slip-forming, and will provide the front of the ground floor. Finally, the researchers use robots and spatial timber assemblies to prefabricate the top two floors.
By next year, the building will be ready to use as a place for Empa and Eawag guest researchers and partners of NEST to work and relax. However, there’s still a lot of work to complete first — head over to the DFAB website to find out more.
Source: DFAB
License: The text of "Swiss Researchers Begin Construction of the DFAB HOUSE" by All3DP is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
